Changelog¶
v 3.23.0¶
Plan Generator¶
A new module has been introduced: the plan generator! This module can assist in generating DICOM RT plan QA files customized for your clinic. It can produce basic shapes and typical QA fields such as picket fence, open fields, and more. See the Plan Generator section for more.
RT plan fluence can be plotted using a new function:
plot_fluences(). This will plot the fluence of the plan fields as figures. This is useful for visualizing the plan fluence and comparing it to the expected fluence. This can be used in conjunction with the plan generator to visualize the fluence of the generated plan. See Plotting Plan Fluence for more.
Picket Fence¶
The HDMLC arrangement was changed from 10x40x10 leaves to 14x32x14 leaves to match reality. This may affect the max leaf error metric slightly. In our tests, the change did not skew positive or negative. The mean change was approximately 0.05mm. While changing a definition is not desirable, matching the actual configuration is more important. If for some reason you need the old configuration, you can create a custom MLC arrangement. See the Customizing MLCs section.
The leaf error barplot to the right/bottom of a picket fence plot was somewhat confusing. It would show the mean and standard deviation of the error, but not the entire distribution. This plot has been converted to a normal boxplot, showing the median, Q1, Q3 and flier data. More about the boxplot can be read here: boxplots.
The leaf error subplot that shows up at the right/bottom of the analyzed image now shows leaf numbers instead of pixels.
A new method is available
plot_leaf_error. This method will create a figure of the leaf error boxplot. This is similar to the leaf error subplot that shows up at the right/bottom of the analyzed image, but can be called independently.
Core¶
Pylinac is meant to be compatible with all Python versions still in security lifecycles, which is currently 3.8. Some syntax was introduced that was not compatible with Python 3.8. This has been fixed. Note that Python 3.8 will be EOL in October 2024. The next pylinac release after that will drop support for Python 3.8.
v 3.22.0¶
Field Analysis¶
#485 Analysis for the Profiler device would swap the 30th and 31st detector positions, possibly causing flatness and symmetry calculation errors depending on the slope of the profile. Steeper slopes would have a larger effect. To match SNC profiler software and RadMachine, these detector values have been removed.
The x-axis of the field analysis when using a device has been shifted by 1 to reflect the “detector” label accurately; it used to be 0 which is non-sensical for physical detector number. This will also match SNC Profiler software for detector number. Finally, the y-axis label now says “Response” vs “Normalized Response” since the normalization can be a variety of options.
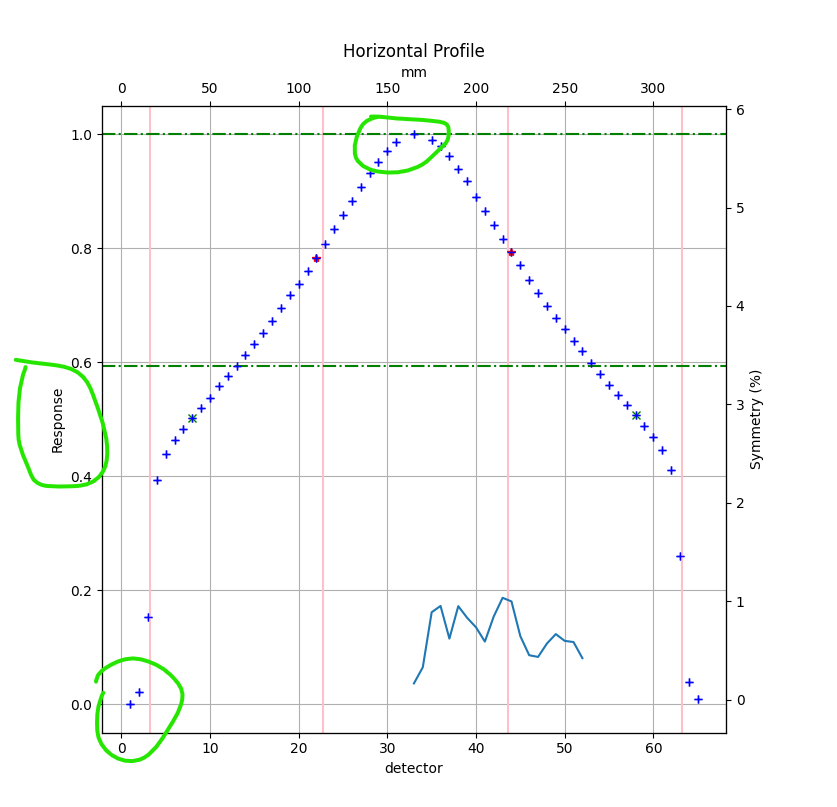
Image Metrics¶
The
GlobalSizedDiskLocatorclass has added aninvertparameter. This parameter existed for the other locators, but was missing for the global disk locator. Previously, the locator was always inverting the image (assuming images like EPID). Now, the parameter can be used to control this behavior. By default, the parameter is true for backwards-compatibility.
Profile Metrics¶
A new metric has been added:
SlopeMetric. This will calculate the in-field slope, similar to NCS-33. This is useful for calculating the slope of a field, notably FFF fields as an alternative to flatness.
Image¶
It is now possible to save
XIMimages back to a simplified DICOM dataset. A new method has been added:as_dicomwhich will return a pydicom Dataset.When plotting an image (
DicomImage,ArrayImage, etc) where metrics had been computed, the metrics would be plotted on the resulting figure all the time. A new parametershow_metricshas been added to theplotmethod to control this behavior.
Core¶
Users can now export analysis results as JSON. This is helpful for dumping results to file or for use in passing data to another library or program. A new topic page is available: Exporting Results.
CT¶
The
CTP486results data section for CatPhan analyses added the keysnps_avg_powerandnps_max_freq. These are the average power and maximum frequency of the noise power spectrum, respectively.
Winston Lutz¶
The Winston-Lutz algorithm has been updated and generalized. More work is happening for multi-field and multi-target and single-field analyses. The BB-finding and field-finding is now generalized for the cases of N targets and M fields. For multi-target/multi-field analyses, the algorithm was very memory-intensive because it was creating X*Y analysis objects where X is the number of images and Y is the number of targets. Memory usage has been reduced from this refactor.
The class
WinstonLutz2DMultiTargethas changed toWinstonLutzMultiTargetMultiFieldImage. Unless you are using the class directly, this change should not affect you.The
plot_images()method has changed. Instead of returning N figures where N is the number of BBs where each figure is a set of plots for each BB, M figures are returned where M is the number of images. Each plot will show the image and all detected BBs and fields. This gives better context about which BB was detected where as it relates to the image as a whole. Images within PDFs will also be generated in the same way.For MultiField analyses, the
cax2bb_distance()andcax2epid_distance()metrics were giving artificially high values when the metric wasmedianormean. This was because the metric was first calculating the maximum distance for a given image, and then taking the median or mean of those values. This was not the intended behavior. The metric now calculates the median or mean of all the distances for all BBs together. I.e. it was doingmedian(max(a1, a2, a3), max(b2, ...), ...)instead ofmedian(a1, a2, b1, b2, ...). This will result in lower values for the metric compared to previously.Plots now show a legend of the EPID, BB, and field CAX. The legend can be turned off by passing
legend=Falseto theplot_imagesmethod.Plots are now zoomed to fit all the BBs/fields detected. In the simple case of a single BB at isocenter, this hasn’t changed. For multi-target/multi-field WL, the plots will now be zoomed to fit all the detected BBs and fields. This can be turned off by passing
zoom=Falseto theplot_imagesmethod.When using custom BB arrangements, use the new
BBConfigclass instead of a dictionary. See the updated Custom BB Arrangements section for more.A bug was fixed for the BB shift vector/instructions when analyzing images with couch kicks. The Low paper which contains the mathematical transforms appears to have incorrect signs in equation 6. This has been fixed and validated using the new image generator ability to create images with couch kicks. The bug was causing the BB shift vector to be incorrect when analyzing images with couch kicks. The shift errors were always in the LAT/LONG plane and for the most part underestimated the shift that would be needed.
For regular WL analyses, a virtual shift can be automatically applied to the BB to see what the 2D errors would be if the BB were shifted to the optimal position. Read more in the Virtual Shifting section.
For multi-target/multi-field analyses, the BB shift vector is now available as the
~pylinac.winston_lutz.WinstonLutzMultiTargetMultiField.bb_shift_vectorproperty. This provides a 6DOF shift vector that can be applied to the BB to move to the ideal position. These shifts are also included in theresults_data()call.The 3D plotting of BBs in virtual space for both single-target and multi-target analyses has been reworked. For single-target WL, the green isocenter lines used to always be at the origin. The lines represented the field-determined isocenter. To better represent the field isocenter, bb isocenter, and the EPID isocenter, and their relationships to each other, the origin is now the EPID-based isocenter and the green x/y/z lines are the field isocenter. This makes it possible to see the BB and field isocenters in relation to the EPID isocenter as well.
Couch-kick images are now supported for multi-target analyses. They are included in the BB shift vector calculations as well.
Couch-kick images are also analyzed for the 2D yaw error on each image. These are included in the
results()call.The multi-target/multi-field demo dataset was changed to purposefully introduce error for a more realistic demonstration.
Image Generator¶
A
SlopeLayerhas been added. This will apply an image-wide slope to the image. This can be useful for introducing asymmetry to a synthetic image.The image generator can now create images with collimator and couch rotation. For cone-style layers (e.g.
PerfectConeLayer) the rotation is about the center of the image and for all intents and purposes is a couch kick. For field-like layersPerfectFieldLayerthis simulates a collimator rotation.The Winston-Lutz image generator will respect and apply collimator and couch rotations when generating images based on the
image_axesparameter. E.g.(90, 45, 15)will generate an image with gantry and 90, collimator at 45, and couch at 15 with the BB and field aspects corrected for these rotations.The Winston-Lutz image generator has a machine scale input.
v 3.21.1¶
VMAT¶
A bug in the VMAT analysis was causing apparent shifts in the ROI position. This would happen if the gaps between the ROIs were below 50% of the maximum. The ROI position is now based on the center position of the open field rather than the center of the DMLC image. This caused a shift in some of the ROI positions of the test images of a few pixels (2-7 pixels). This also caused the ROI values to change by anywhere between 0 and 0.2% in our test suite.
This same bug was causing identification issues of open vs DMLC images occassionally, usually for Halcyon datasets. The identification algorithm has been adjusted to better detect these scenarios.
v 3.21.0¶
Contrib¶
A new contrib module has been added to pylinac: One-Offs. This section is available as pylinac.contrib.
The intent is for community-contributed modules and/or one-off analyses that are not part of the core
library but are still useful. So far, many RadMachine customers have asked for one-off analyses.
While I disagree with adding one-off analyses to the core library, I also don’t want to let the
code be in secret for no good reason.
VMAT¶
The VMAT image identification algorithm was changed slightly to better detect FFF DRMLC/DRGS images.
CT¶
Warning
In the last release, the noise power spectrum was not being calculated correctly. We recommend re-running analyses that were using NPS values.
The noise power spectrum introduced last version was not working correctly. The NPS was not subtracting the mean value from the ROI. This has been fixed. However, as a result of reworking the calculation, the NPS now has its own module:
pylinac.core.nps. This contains several modules for independent calculation of the NPS and associated metrics like average power, etc. See Noise Power.The NPS is now calculated over square ROIs approximately the same size as the circular uniformity ROIs rather than one central ROI. This is because the resulting spectra is smoother when averaged using multiple, separate ROIs.
The
power_spectrumproperty of the CTP486 module has been renamed topower_spectrum_2dand another property,power_spectrum_1dhas been added.CT scans with overlapping slices AND without the
SpacingBetweenSlicestag were failing. The slice spacing distance will now use the distance betweenImagePositionPatienttags of the first two slices to avoid reliance on theSpacingBetweenSlicestag.
Picket Fence¶
Picket fences where only a relatively small subset of the leaves were being analyzed (e.g. 10 pairs) were sometimes failing. This would produce a
ValueError: cannot convert float NaN to integererror. This has been fixed. As a workaround, often the fix was to setrequired_prominenceto a small value or None. This is no longer necessary.required_prominencenow reflects the normalized height (0-1.0) the pickets should be above the background. Previously, this value was not normalized, requiring fiddling with the value to get correct and depending on the number of leaf pairs that were being analyzed. The number of leaf pairs should no longer be a factor in the analysis.
Image Metrics¶
Disk-finding metrics, such as Winston-Lutz, had a bug that would cause disks to not be found if the image size was smaller than the search window. This happened if the image size was ~<=3x the BB size. I.e. if the image was 200x200 pixels and the BB was 70 pixels, the search window sampler would not correctly size the window. This was only found to affect users of small pieces of film.
The
SizedDiskRegionandSizedDiskLocatorclasses now have amin_number,max_number, andmin_separation_<pixels|mm>parameters, as theGlobalSizedDiskLocatorclass does. This allows the user to specify the minimum and maximum number of disks. Previously, theSizedDisk<Region|Locator>classes would only find one disk.Warning
This change also means that
SizedDiskLocatorandSizedDiskRegion’scalculatemethod will now always return a list of Points or ROIs. Previously, a single Point or ROI was returned. This change will break code that was expecting a single Point or ROI.
Core¶
The
DicomStack.from_zipclass constructor now accepts**kwargswhich will pass to the normal constructor.
v 3.20.0¶
Core¶
The function
image.load_multiplesnow accepts aloaderparameter. This lets the user pass a custom image class if desired. This is useful for subclasses of the base image classes. E.g.image.load_multiples("my_image.dcm", loader=MyDicomImage). Default behavior still usesload.Plotting the MTF was causing an zero division error or warning. This was from the plotting of the line pair distances in addition to the frequency.
Picket Fence¶
The
from_multiple_imagesmethod signature added themlckeyword argument. Previously, only the default MLC could be used.Picket fence plots were being plotted upside down. They will now be plotted right-side up.
The MLC arrangement for Varian machines was inverted. Leaf 1 was assumed to be at the top of the image, but it is actually at the bottom. This will affect both the combined and separated leaf analysis. An error that would’ve shown, e.g., A20 will now show A40.
The MLC skew is now reported in the
.results()method.
Winston-Lutz¶
Image inversion checking is now done during the analysis phase and not during image loading. This is mostly for RadMachine to allow users to apply manipulations first, and then perform typical image processing, including inversion checking. Unless you are performing image inversion manually between the class instantiation and the
.analyze()call, this change should not affect you. If you are, you may no longer need the inversion call.
ACR¶
The slice thickness given when calling
ACRMRI.results()was reporting the nominal slice thickness not the measured slice thickness. The output fromACRMRI.results_data()was correct however and has not changed.
v 3.19.0¶
Core¶
The efficient DICOM stack introduced in the last version did not allow for writing images back to the stack (e.g. when manipulating the image). Images can now be written back to efficient stacks.
RectangleandCircleclasses have a new property:area. This will return the area of the shape.
Nuclear¶
A new module has been created. This module is a Python implementation of the NMQC toolkit for SPECT. It contains 9 tests that are very similar to the ImageJ toolkit. See Nuclear for more.
CT¶
Publishing a PDF for the 604 and 600 sometimes led to the HU module values falling off the right side of the page. The values are now wrapped and should all fit on the page.
The noise power spectrum is now available for CatPhan analyses. See more here: Noise Power Spectrum.
The CT phantom-finding algorithm is now slightly more robust to inclusion of the table in the scan. Foam or other low-density material is still recommended to separate the phantom from the table.
Analysis of Catphan 604 datasets often did not find the HU module center correctly. This had to do with some of the HU plugs being longer than the rest of the features in the 604 model. This was not causing issues and was left as-is for quite some time. However, several RadMachine customers had noticed the slice thickness may be different because of this. The algorithm has been adjusted to find the center of the HU plugs more accurately by performing a second pass over the center slices using the relative angle between the wire ramps. This only affects the Catphan 604. Users may notice a small change in HU values since the slice may now be different by 1-3 slices. Users may also notice a change in the slice thickness value. All test dataset results either stayed the same or were closer to the nominal value. Contrast values may also change slightly. Each of the modules are now almost always centered on the top bright marker above the module.
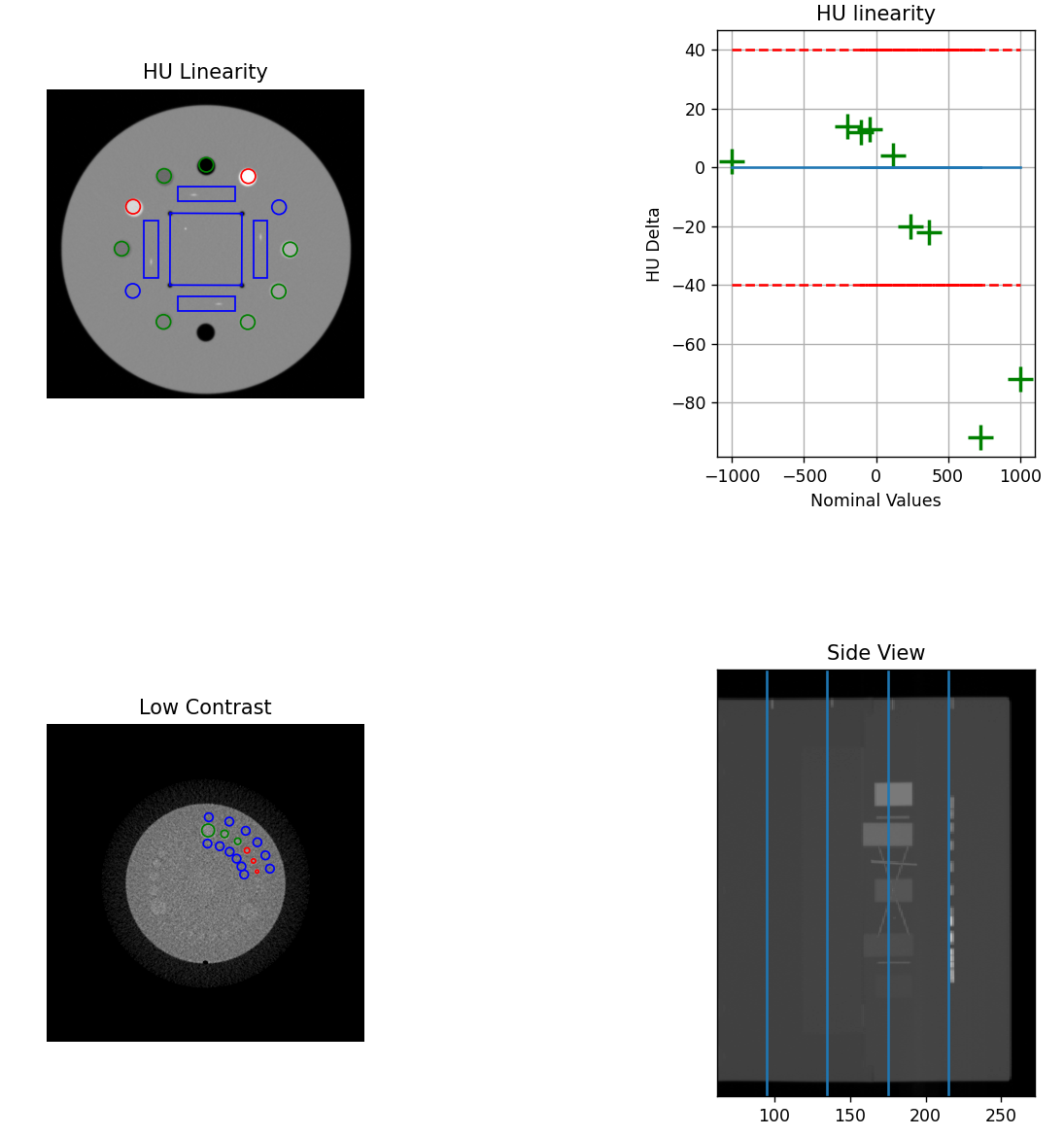
The old algorithm. Note the wire ramp is on the left side of the ROI for the top position. This indicates we are not at the center of the HU module. Also note the side view line is barely off-center to the left for the HU module.¶
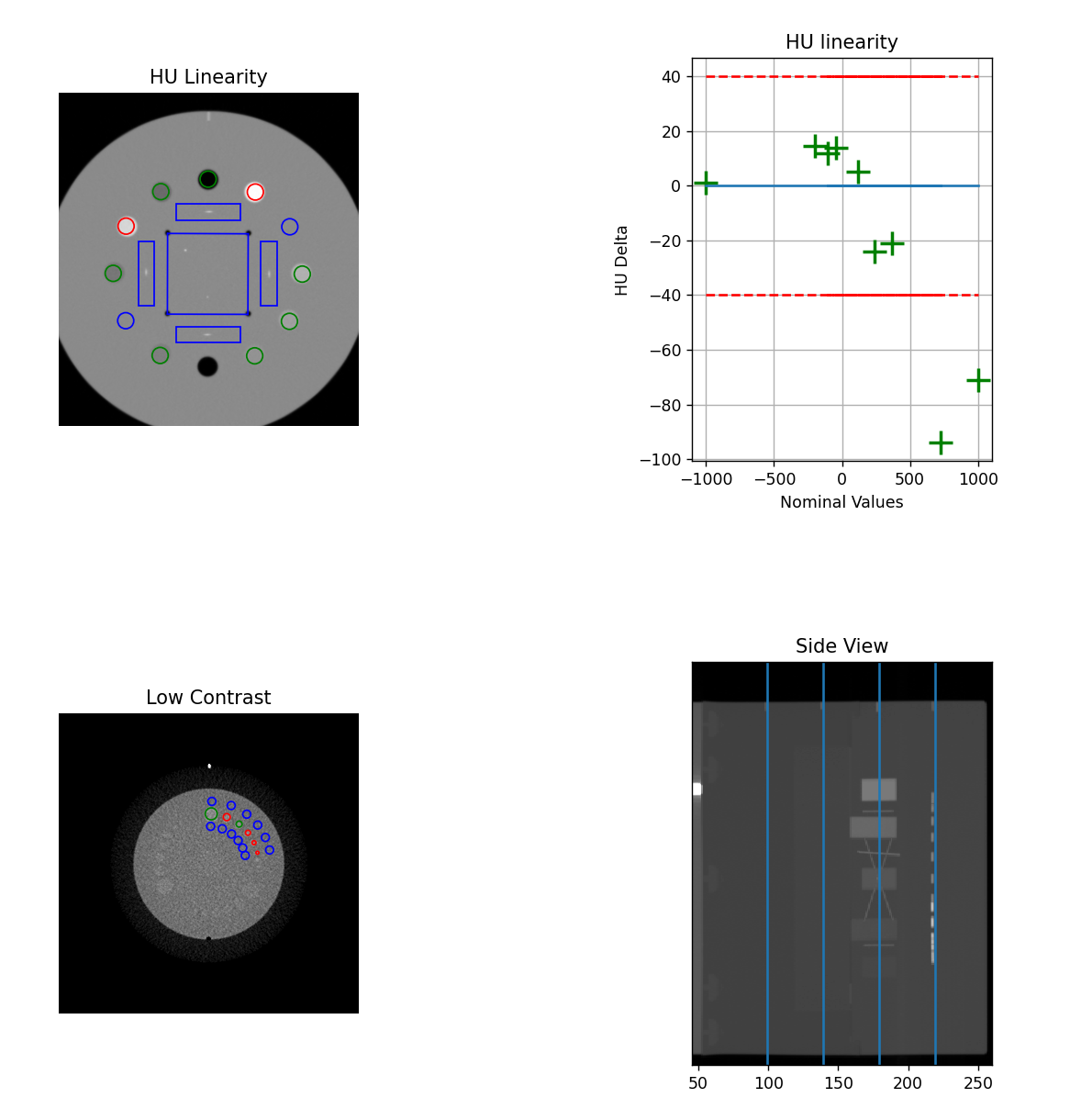
The new algorithm. Note the wire ramp is now in the center of the ROI for the top position. This indicates we are at the center of the HU module.¶
Due to the above change, a new method is available to override if desired:
refine_origin_slice(). This method will perform the second pass over the center slices to find the HU module center. This method is available for all Catphan analyses and will be empty for all phantoms besides the 604 for the time being.If the old behavior is desired, the
refine_origin_slice()method can be overridden to simply pass the initial slice number:from pylinac import CatPhan604 class MyCatPhan604(CatPhan604): def refine_origin_slice(self, initial_slice_num): return initial_slice_num
Profiles¶
Physical profiles
...ProfilePhysicalnow have aphysical_x_valuesproperty. This will return the x-values in physical units. This can be useful for plotting the profile in physical units if desired.Physical profiles
...ProfilePhysicalnow have aas_simple_profilemethod. This will create a new profile of the same type minus the physical (e.g.FWXMProfilefor aFWXMProfilePhysical) that has its x-values set to the correct physical values. This can be useful when wanting to compare, say, an EPID physical profile with an ion chamber profile, where the x-values of the IC profile are already in absolute physical units.Profiles have a new method to make comparing one profile to another, point-for-point, easier:
resample_to. This method will resample the profile to the x-values of another profile. This is useful for comparing profiles point-by-point, such as for a 1D gamma evaluation.
Planar¶
Planar phantom analyses now have a
phantom_areaproperty available. This is also available in theresults_datamethod. This area is useful to test scaling of the image. See Scaling for more.The
DoselabRLfandStandardImagingFC2phantom analyses have had their BB-finding search box changed from 10mm to 8mm. This increases the robustness slightly as a few datasets were failing due to catching a larger chunk of the field edge due to the larger box search size.There is a new parameter for light/rad phantom analysis:
bb_edge_threshold_mm. This parameter controls the BB-finding algorithm. If the expected position of the BB is less than this threshold, a more robust BB-finding algorithm is used. This is useful when the BB and field edge are harder to differentiate.Light/Rad phantoms have a new class parameter:
bb_size_mm. This sets the expected size of the BB. This shouldn’t have to be changed from the default except for new phantoms.The BB-finding algorithm has been changed from an ad-hoc algorithm to use the new
metricsmodule’sWeightedCentroidclass. Some test datasets had results that changed by a few tenths of a mm. This is largely from using the weighted centroid vs the centroid of the original algorithm. Due to using this metric, the BB detection outline will also now be plotted.
v 3.18.0¶
Picket Fence¶
The
from_multiple_imagesmethod now no longer uses the demo image as a placeholder. This was causing an error when using this method within RadMachine as it was trying to load the demo image.A new method is available for picket fence instances:
picket_width_stat. This will return a statistic for a given picket. This is useful for determining the consistency of the MLCs.A new item is available in
results_data:picket_widths. This metric will provide the max, min, median, and mean of the picket widths for all MLC pairs across a picket. This is another way to test MLC consistency.
CT¶
CatPhan, Quart, Cheese, and ACR phantom analyses now have a new parameter option:
memory_efficient_mode. This mode will use dramatically less memory than the default implementation. This is useful for large datasets or limited resources on the machine running the process. This does come at a ~25-80% speed penalty depending on the size of the dataset. Larger datasets will have a larger penalty.In the
resultsmethod, the CTP528 (spatial resolution) and CTP486 (uniformity) sections have been swapped. This is so that the resulting PDF text and images on each page matches. Previously, the PDF text and images for these two modules were switched.
Winston-Lutz¶
The
results()method of theWinstonLutzclass will now also report the mean distance from the BB to the CAX in mm.The Winston-Lutz algorithm now uses the new
SizedDiskLocatorinternal class (see below). This was introduced in pylinac 3.16. The algorithm is very similar to the existing WL algorithm.A new parameter has been added to
analyze():bb_tolerance_mm. This gives an acceptable window for finding a BB. E.g. if the BB size is 2mm, the tolerance can be set to 1mm. Alternatively, if the BB is very large, the tolerance can be widened. This was done since very small and very large BBs were sometimes tripping up because of the hardcoded 2mm tolerance. The default tolerance is still 2mm.Important
If you use WL with very small BBs (<3mm), we recommend you set the tolerance to 1mm.
The BB boundary is now plotted. See the “Metrics” section.
Detection conditions for the WL algorithm can now be set via the
detection_conditionsparameter forWinstonLutz2Dand set as a class attribute forWinstonLutz.Important
As always, pylinac uses the weighted centroid of the detected pixels. If the boundary seems to include an extraneous pixel, it should minimally affect the BB location.
Metrics¶
There is a new
metricsmodule in pylinac. Existing metrics have been moved into this module.E.g. instead of
from pylinac.core.metrics import SizedDiskLocatoryou would now dofrom pylinac.metrics.image import SizedDiskLocator. Image-based metrics are now underpylinac.metrics.image. Profile-based metrics are now underpylinac.metrics.profile. Individual feature detection functions are now underpylinac.metrics.features.For backward compatibility (even though metrics are relatively new feature), the old import locations will still work but will raise a deprecation warning.
The documentation for metrics has been updated considerably. See Images & 2D Metrics.
The detection algorithm for disk/field metrics has been written out; see Algorithm.
The
DiskLocatorclass was renamed toSizedDiskLocator.The
DiskRegionclass was renamed toSizedDiskRegion.The
GlobalDiskLocatorclass was renamed toGlobalSizedDiskLocator.The
SizedDiskLocatorclass now plots the detected boundary of the disk/BB. Because the WL algorithm now uses this class, the WL plots now also include the detected BB boundary.A new metric class has been added:
GlobalFieldLocator. This class will find a number of open fields within an image without having to know the field size beforehand. See Global Sized Field Locator for more.Previously, metrics would allow the image to be modified. The metric would copy the image temporarily. However, a memory bug would cause large numbers of images to use inordinate amounts of memory. Now, images cannot be permanently modified. A hash check will be run before and after the calculation to ensure the image array has not been modified and will raise an error if it has.
Calling
plotnow allows to pass ametric_kwargsparameter. This allows the user to pass arguments to the underlying metric’splotmethod. This is useful for customizing the plot.A new metric
PDDhas been added. This will calculate the percent depth dose at a given depth using a polynomial fit.A new metric
Dmaxhas been added. This will calculate the maximum dose using a polynomial fit.Profiles will now be sorted to have the x-values always be increasing.
A bug was fixed when descending x-values for a profile were passed. This was causing the center index to be faulty.
v 3.17.0¶
Metrics¶
Another metric is now available for 2D image analysis:
GlobalDiskLocator. This metric will find a number of BBs/disks within an image. This is useful for finding BBs in an image without knowing where they might be. This is relatively efficient if there are multiple BBs in the image compared with using theDiskLocatorclass multiple times, even when the BB locations are known.The metric
GlobalSizedFieldLocatoris also available. This metric will find a number of open fields within an image. See Global Sized Field Locator for more.
Planar Imaging¶
A new method is available for planar phantom analyses:
percent_integral_uniformity(). This method will calculate the percent integral uniformity (PIU) over the low-contrast ROIs. This result will also be included in theresults_datastructure. This is not done for light/rad phantoms.If a phantom had a completely homogeneous array for an ROI, the
results_datacall would fail due to a division by 0 error. This has now been fixed such than an error is not raised. However, the resulting CNR and SNR will be a special case offloat('inf'). This was encountered with a very low kVp analysis of the Doselab MC2 kV/MV phantom.
Picket Fence¶
The Halcyon MLC configurations were incorrect and have now been fixed. Thanks to Dominic Rafferty for pointing this out. Previously, it was using a similar configuration as the TrueBeam out of lack of experience with the system. The new configuration was based on this paper.
Winston-Lutz¶
Normal Winston-Lutz analyses (not multi-target/multi-field) can now plot a visualization of the BB position relative to the determined isocenter. After analyzing a WL set, call
plot_location(). See Visualizing the Isocenter-to-BB.
CT¶
A new class
CIRS062Mis now available. This will analyze the CIRS electron density phantom.The base class for cheese phantoms (
CheesePhantomBase) now has a default implementation forresults_data. Previously, it did not and required the user to create one when extending the phantom analysis to a new type.The
TomoCheesephantom’s output fromresults_datahas an additional key:rois. This is a dictionary of all the ROIs with the name of the ROI (usually the number) as the key. The data in theroisdict is the same information as in theroi_<n>elements. In retrospect, a simple dictionary is far more extensible when the number of ROIs vary. I.e.results_data()['rois']['1']is the same asresults_data()['roi_1']. Theroi_<n>keys were left for backwards compatibility.A new class
HypersightQuartDVThas been added that will analyze the Hypersight variant of the Quart phantom, which includes an additional water ROI.
ACR¶
The
z_positionproperty for DICOM stacks (used in CT and MRI) was usingSliceLocationif the tag existed andImagePositionPatient[-1]if it did not exist. TheSliceLocationtag however is apparently relative. This caused problems for the ACR MRI module on properly-acquired datasets. TheImagePositionPatienttag is now the primary lookup key andSliceLocationis only used if the former tag is unavailable.
Starshot¶
The
from_multiple_imagesmethod no longer requires the demo image. The demo image was just a placeholder to set up initial values.
Profiles¶
The following applies to the SingleProfile classes:
Passing decreasing x-values to
SingleProfilewould usually result in an error because the measured width would be negative. An error will now be raised if the x-values are decreasing.Profiles that had non-integer increments in the x-values were not returning the right field values. I.e. when calling
.field_data()['field values']and non-integer x-values were passed at instantiation the values were not correct. Given theSingleProfileclass is now frozen, it is recommended to not pass non-integer x-values and/or skip passing x-values to the profile.
The following applies to the <FWXM|InflectionDerivative|Hill>Profile classes:
The same error of passing decreasing x-values as above was also detected in the new
<FWXM|InflectionDerivative|Hill>Profileclasses. Given these classes are the new standard, they have been fully fixed and can now handle decreasing x-values.Profiles that had non-integer increments in the x-values were not returning the right field values. I.e. when calling
.field_values()and non-integer x-values were passed at instantiation the values were not correct. This has been fixed.The
x_at_xmethod has been renamed tox_at_x_idx. A deprecation warning will be raised. The method will be removed in 3.18.The
y_at_xandx_at_yandx_at_x_idxmethods now all return a numpy array instead of a float.A new method has been added:
field_x_values. This returns a numpy array of x-values that corresponds to the y-values that are returned when usingfield_values. This is useful for plotting the field values to the correct x-values.The
SymmetryPointDifferenceMetricclass’ plot method now uses “x” for the markers instead of “^” and “v”.
v 3.16.0¶
Planar Imaging¶
results_datafor planar imaging phantoms (Leeds, SNC kV/MV, Doselab MC2, etc) will now return alow_contrast_roisdict that contains relevant info for each low-contrast ROI.
Winston-Lutz¶
The Winston Lutz module can now load CBCT datasets of a scanned BB. This is still experimental and may have bugs. Caution is warranted. See CBCT Analysis.
CBCT¶
Passing expected HU values for ROIs is now much easier by passing a dictionary to the
.analyze()method. See Custom HU values.
Profiles¶
Profile analysis has been completely revamped. The existing
SingleProfileclass still exists and will not be deprecated immediately. It is frozen and will not receive updates.New profile classes were written that are more generalizable and extensible. These can be read about in the documentation below.
The new profile classes also have a new plugin system for computing custom metrics. This allows for much more user-friendly, readable, and extensible code for both myself and users.
A new documentation section has been added for profiles: Profiles & 1D Metrics. This section describes the various profile classes and how to use them.
Internally, pylinac now uses these new profile classes. Existing calculations should be the same.
Calculating custom profile metrics (such as symmetry or flatness) is now much easier using these new classes. The field analysis module will get a “v2” that will use these new classes and allow for these easy-to-write custom metrics.
Core¶
Image¶
Similar to the new profile plugin architecture, 2D images also have a new plugin metric system. See the new documentation: Images & 2D Metrics.
The
DicomImageclass has a new class method:from_dataset(). This allows one to create a Dicom image from a pydicom dataset directly.
Image Generator¶
The
Simulatorclass and its subclasses has a new method:as_dicom(). This method will perform the same action asgenerate_dicom, but instead of saving to file, will return the pydicom Dataset.
v 3.15.0¶
Winston-Lutz¶
For the MultiTargetMultiField Winston Lutz analysis, non-zero couch angles are not allowed. However, the check for this was limited to 0-5 degrees. Couch values that were on the other side of 0 were not being included. Couch angles between 355-5 degrees are now allowed as originally intended.
Planar Imaging¶
The Doselab RLf light/rad phantom has been added as an analysis options: Doselab RLf.
The IsoAlign light/rad phantom has been added as an analysis options: IsoAlign.
CT¶
The catphan detection was failing if the phantom jig was touching the phantom at the center of a module. This has been fixed.
A rounding error was fixed where the extent check was failing because of floating point rounding differences. This was causing an error to be raised when the scan extent was just slightly smaller (or appeared to be smaller) than the configuration extent.
ACR¶
The ACR MRI phantom analysis was sometimes failing because the slice thickness check was failing. This was caused by a slightly inappropriate use of the profile module, causing instability under certain conditions. The MRI analysis should be more stable. Quantitative results should be the same.
VMAT¶
The standard deviation for each VMAT segment is now available as the
.stdevproperty of the segment.vmat = DRMLC(...) vmat.analyze(...) data = vmat.results_data() print(data.segments[0].stdev) # first segment stdev
Core¶
When saving a DICOM image, the pixel values were not “unscaling” the raw pixel values. I.e. the scaled values were being saved back to the DICOM file. If the image was then read in again, the values would be scaled twice. This has been fixed and DICOM images can now, for the most part, go “round trip” without the raw pixel values changing. An example is below:
dcm_image = image.load("my_image.dcm") dcm_image.array # this is scaled by the DICOM tags dcm_image.save( "my_output_image.dcm" ) # the pixel values were written back *as rescaled* dcm_image2 = image.load("my_output_image.dcm") dcm_image2.array # this was scaling by the DICOM tags *again*
Warning
If the DICOM pixel values have been modified, such as concatenating images together, and the values are too high or too low for the original datatype (usually uint16), the values will be scaled to fit the datatype, with the maximum value being the max of the datatype. A warning will be raised when this occurs.
Most of the time these operations are relative and absolute values don’t matter, but it’s still something to be aware of.
v 3.14.0¶
Planar Imaging¶
An Elekta variant of the Las Vegas phantom has been added:
ElektaLasVegas.The SSD parameter of now defaults to “auto” (
.analyze(..., ssd="auto")). Previously, it was set to 1000mm. If “auto”, the phantom is first searched at 1000mm (for backwards compatibility). If the phantom isn’t found, it then searches at 5cm above the SID value. The 5cm is to account for the physical shroud of most EPID panels. If the phantom isn’t found at either of these locations an error is raised. In that case, the SSD should be provided manually, which was already the case previously.
CT¶
CBCT, ACR CT/MR, and Quart analyses will now plot a “side view” of the phantom with lines to show where the modules were sampled. This will help visualize if the module slice selection was appropriate.
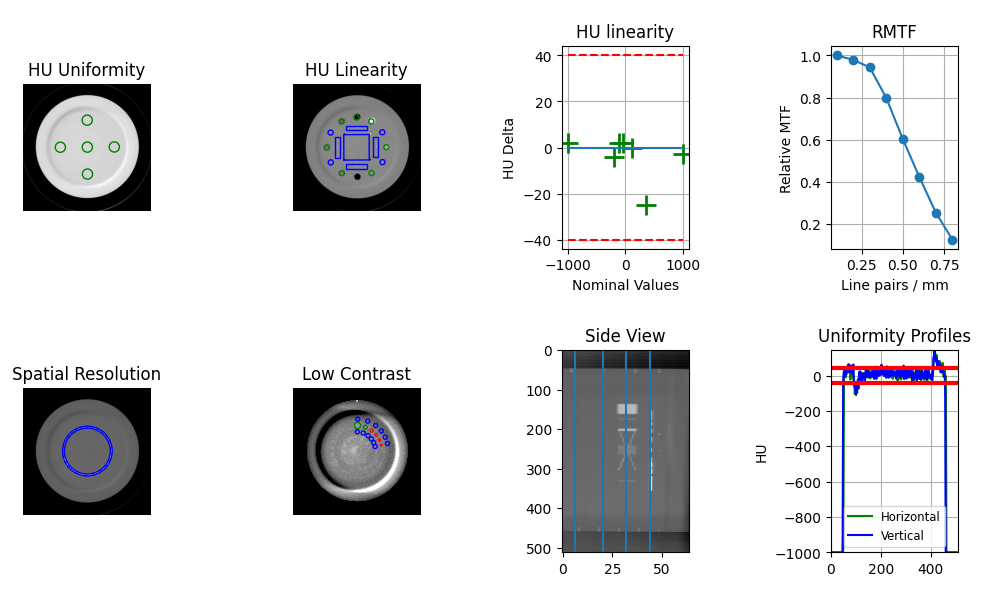
A new check for the scan extent vs the configuration extent is now in place. This will check that the physical extent of the scan is large enough to include all the listed modules. If it’s not an error will be raised. This improves the error diagnosis when a scan did not include enough data.
Note
This applies to all CT-like algorithms including the ACR analyses.
ACR¶
The ACR MRI algorithm now accounts for scans where slices do not abut. E.g. if the slice thickness is 5mm and the spacing between slices is 10mm.
The ACR MRI high-resolution ROIs have been adjusted slightly to match the increasing test suite data, however, there are still some sets that do not perfectly align. We suggest following the Customizing MR/CT Modules section and adjusting the location as needed.
The ACR MRI algorithm has a new parameter for
analyze:echo_number. This lets the user pick an echo number if the acquisition was a dual echo scan. This is not required however. If the scan is dual-echo and no echo number is passed, the scan with the first echo number is selected. See the Choosing an MR Echo.The ACR MRI module classes can now be defined at the class-level, similar to the ACR CT. This was changed so that users can more easily change aspects of each module. See the Customizing MR/CT Modules section for more.
The ACR MRI phantom
MRUniformityModuleOutputhad a typo. The propertyghost_roiswas actually spelledghose_rois. Any code using this property should be updated to the correct spelling.The ACR MRI
results_data()method will now returnROIResultinstances instead of the rawHUDiskROIclasses as before. This behavior already occurs for the catphan module and will thus make the results similar in structure.
Quart¶
The Quart algorithm now measures the high-contrast resolution. It is accessible via the
high_contrast_resolutionmethod. It is given in theresultsandresults_datamethods as well.from pylinac import QuartDVT quart = QuartDVT(...) quart.analyze() high_res = quart.geometry_module.high_resolution_contrast() # or print(quart.results()) # or high_res = quart.results_data().geometric_module.high_contrast_distance
Core¶
The
DicomImageclass has two new properties available:z_locationandslice_spacing. These both apply to CT/MR-like datasets.A new contrast algorithm, “Difference”, has been added. This can be used similar to RMS, Weber, etc. The reason this might be preferred is so that the resulting CNR value is closer to the default algorithm. See Contrast for more.
Contrast values are now case-insensitive. This applies only if you are passing a string for the contrast method.
from pylinac import CatPhan504 from pylinac.core.contrast import Contrast ct = CatPhan504.from_demo_images() # equivalent ct.analyze(..., contrast_method="weber") ct.analyze(..., contrast_method="Weber") ct.analyze(..., contrast_method=Contrast.WEBER)
Image classes (
DicomImage,ArrayImage,FileImage) have a new method:rotate(). This is a wrapper for scikit-image that allows rotation of an arbitrary angle. Previously, only rotations of 90 degrees were allowed via therot90method.The library
cached_propertywas dropped as a requirement since it was introduced in Python 3.8The utility function
find_nearest_indexin theacrmodule was moved tocore.array_utils.The utility functions
abs360andwrap360were moved fromcore.utilitiestocore.scale.
v 3.13.0¶
Warning
As stated in the previous version, v3.13+ will not support Python 3.7. Python 3.8+ is required, matching the PSF’s deprecation policy.
Planar Imaging¶
The Leeds phantom has had its high-contrast ROIs adjusted to better fit the majority of phantoms encountered. Additionally, due to perceived differences in manufacturing, the high-contrast ROIs are now placed according to the center of the high-contrast block. The block is found after the phantom is found and the ROI configuration is adjusted about this center. We have noticed small differences between the block and the phantom center that are large enough to move the ROIs outside the line pairs. Even this however does not correctly place the ROIs all the time.
Warning
This may affect your MTF values, but so far it does not significantly change it if the ROIs were already correctly on top of the high contrast pairs. Images where the ROIs were mis-aligned with the line pairs should now better match, so any change should be between noise and a healthy improvement.
Here are two images comparing the old positions to the new ones for an image that was previously not working:
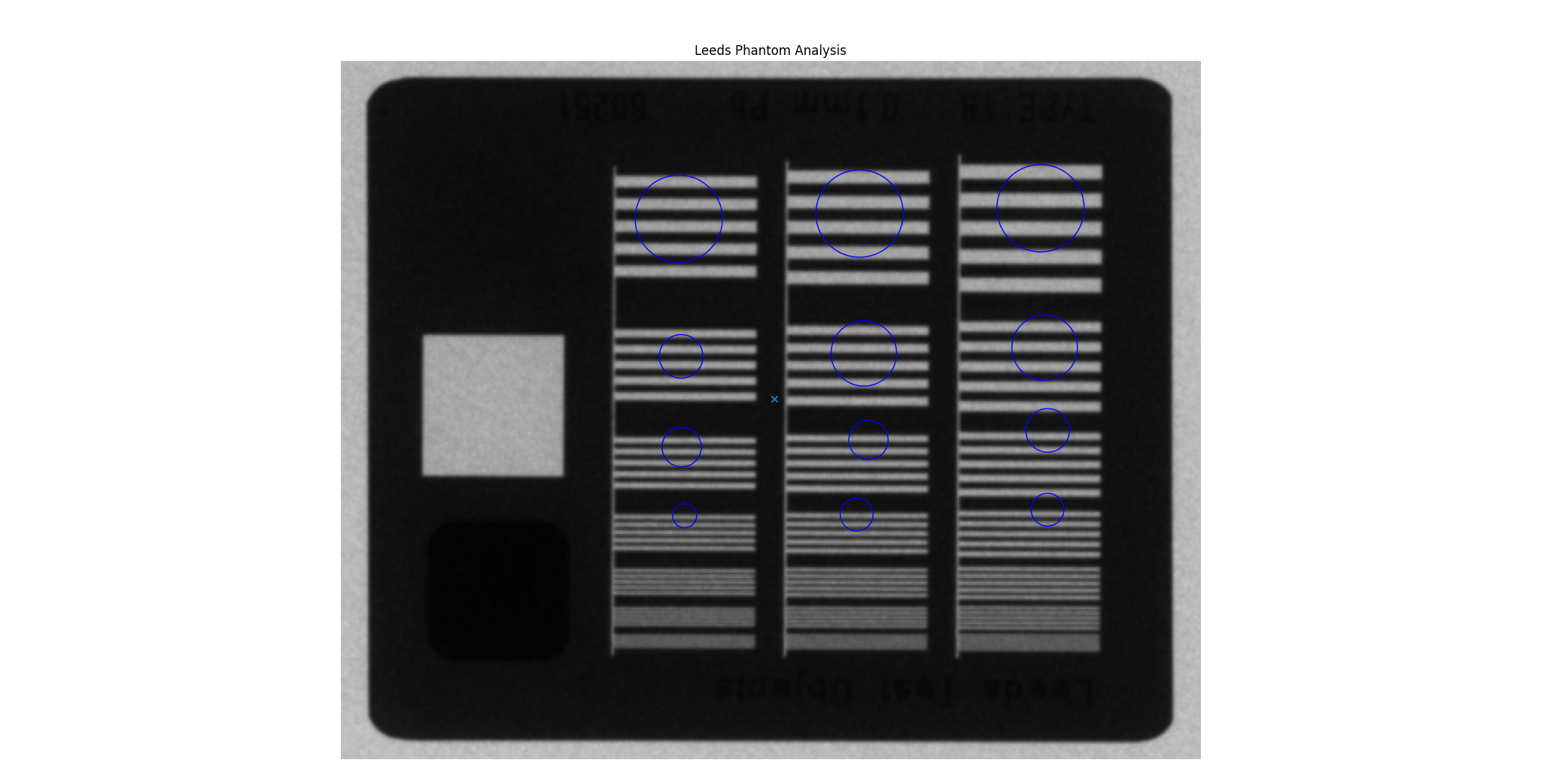

Previous Leeds ROIs on a poorly-fitting image¶

New Leeds ROIs on the same image¶
Here is the demo image, where the ROIs were working before, showing that the new locations still work.

Previous Leeds ROIs on the demo image¶
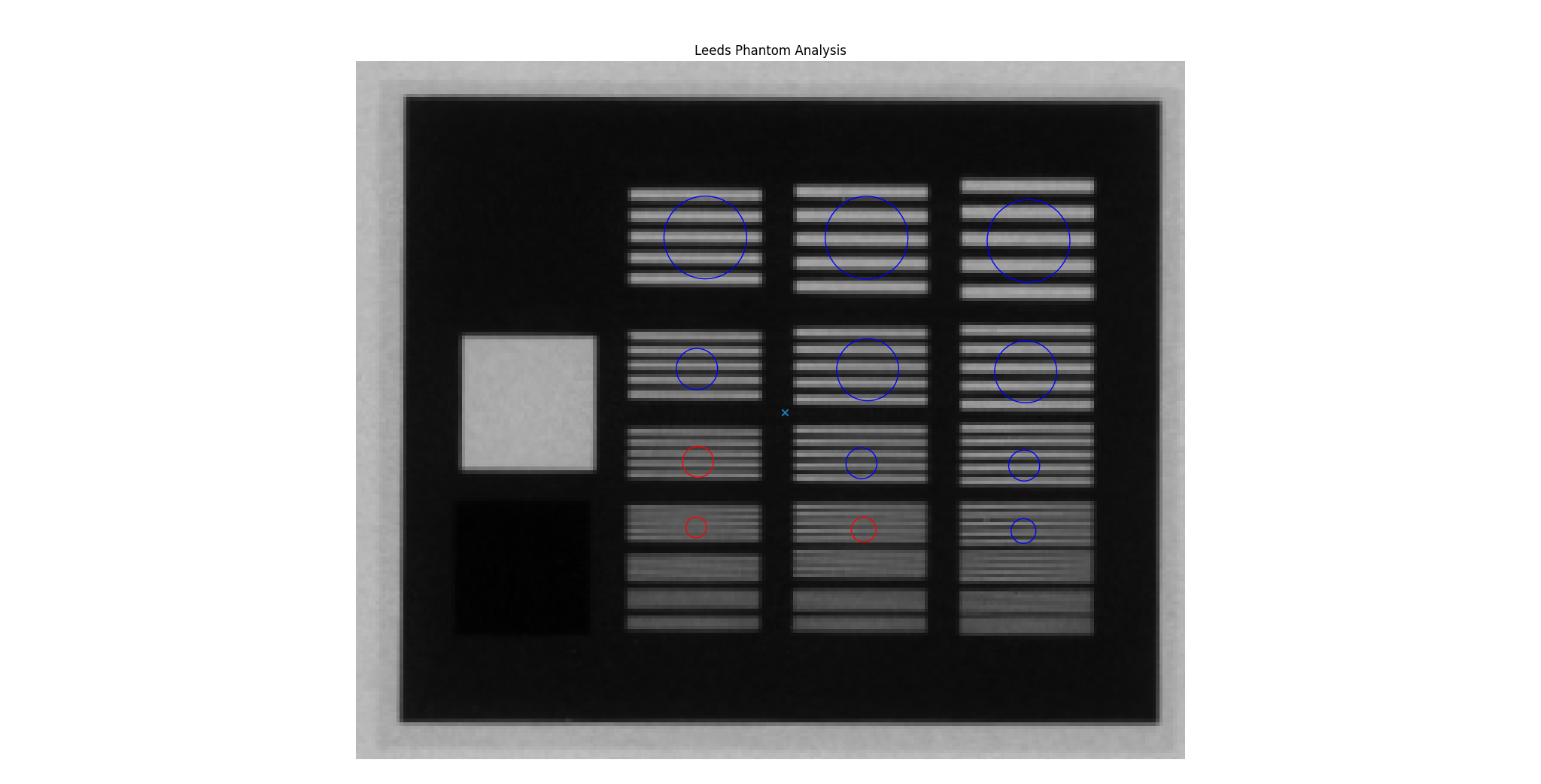
New Leeds ROIs on the demo image¶
Note
At this point in time it’s unclear where the variation is coming from. This is a best-fit solution to this variation. It’s possible there was a revision along the line or the placement tolerances are simply not very tight. We have evidence of other quality issues such as off-center low-contrast ROIs as well. If you know how these differences have come to be let us know!
Finally, if you would like to keep the old ROI locations here is a gist with the old settings: https://gist.github.com/jrkerns/10b62aad7b38c210b9213761447f6155
Related to above, the high-contrast ROIs have been reduced in size slightly so as not to spill out of the line pair area when there are small discrepancies of location. Testing did not change the MTF significantly from reducing the ROI size.
VMAT¶
Three new parameters were added to the
__init__call:raw_pixels.ground, andcheck_inversion. These were added to allow users to avoid applying DICOM pixel correction and analysis manipulations. The reason for this is to match the results from other programs such as Doselab. See the new section Comparison to Doselab.
Core¶
The
DicomImageclass constructor has a new boolean parameterraw_pixels. This was implemented for the above VMAT feature, but can be applied to any image if desired. This will not apply any pixel correction tags, and simpy load the values as saved in the DICOM file.
v 3.12.1¶
Contrast¶
The contrast logic was refactored in pylinac 3.12.0. Unfortunately, this used the “vanilla” definition of weber (see Weber). Pylinac versions 3.11 and prior used the absolute difference of the numerator. Using the signed difference caused issues for existing users and workflows. This was unintentional. For backwards compatibility, the definition has been restored to the previous behavior.
v 3.12.0¶
Warning
This is the last version of pylinac that will support python 3.7 as it will reach end-of-life in July 2023. pylinac v3.13+ will support python 3.8 until October 2024 when python 3.8 is deprecated, etc. You can see the end-of-life chart here.
General¶
The
Contrastclass which contains all the contrast algorithms is no longer an enum. It is now a simple class. This should have no effect on the user unless doing something likeContrast.MICHELSON.value. No changes are required on the users’s part for normal usage patterns.The :ref:<contrast> section has been enhanced to provide more details.
A new core module
contrasthas been created. It contains all contrast-related items. Individual functions can now be called. See the above contrast doc section for examples.A new contrast option is available: Root-mean-square. It is available in the
Contrastclass like the existing options. E.g.leeds.analyze(..., contrast_method=Contrast.RMS)The Image section of the documentation has been enhanced with examples for using the core image behavior.
The
LowContrastDiskROInow provides properties for all contrast types, not just the selected one. I.e.<roi>.weber,<roi>.rms,<roi>.michelson, and<roi>.ratio. The existing<roi>.contraststill exists and will respect the passed contrast algorithm as before. This provides a way to compare other contrast algorithms without needing to re-analyze an image.There was a bug in the
equate_imagesfunction where same-sized images were causing a zero division error. See here: https://github.com/jrkerns/pylinac/issues/446. Thanks to Luis for finding it!The
cropmethod for images had a bug where passingpixels=0would cause the array to diminish to shape 0 along the axes it was cropping.
Winston-Lutz¶
The smallest BB allowed for detection is now ~1mm. This was previously 2mm, but the Varian Exact cube’s BB proved to be too small.
Warning
Setting the BB size to a very small value increases the chance of inaccurately detecting the BB when the BB is encased in a block.
CatPhan¶
A new analyse parameter has been added
thickness_slice_straddle. This is to explicitly control the slice combination technique for the slice thickness measurement. The default behavior is backwards-compatible so no changes are needed. Read more here: Slice Thickness.The parameter
clear_borderswas not being propogated to all submodules for catphan analysis. This is now fixed. Thanks to Chris Williams for finding and fixing the issue here: https://github.com/jrkerns/pylinac/issues/448.
v 3.11.0¶
General/Core¶
The docs now use the
furotheme. 🎉🎉A new function is available under the
imagemodule that converts a TIFF image to a simple DICOM format:tiff_to_dicom().Saving a PDF with the default logo will now additionally try to load the logo from the demo file repository if the file is not available locally. This occurs when using pylinac as a Package in RadMachine. This will now allow users to publish PDFs within RadMachine from a custom pylinac package.
The demo files and PDF references have been removed from the git repository to make shallow clones smaller (e.g. downloading the repo from Github). Demo files are still available publicly as they always have been. No user changes required.
Type errors should no longer occur for older version of Python.
Cheese Phantoms¶
The cheese module has been refactored to be more generalizable so that new cheese-like phantoms can be easily created. Documentation on doing this has been added here.
The
huattribute of theTomoCheeseclass has been renamed tomodule. This doesn’t affect typical use patterns.
Field Analysis¶
Warning
TL;DR: Symmetry will statistically go down and Flatness may rise slightly due to an off-by-one bug. For flat DICOM beams, this is insignificant.
A bug was fixed that caused the data considered to be the “field” to be off-by-one. The last element was not included.
A visualization can be seen here: https://github.com/jrkerns/pylinac/issues/440.
This caused BOTH symmetry and flatness to be affected when using FieldAnalysis and DeviceFieldAnalysis classes.
The value by which the symmetry and flatness will change depends a few factors. The largest factor is the resolution of the original image/dataset. For fields with high resolution, e.g. an AS1200 image, the effects will be smaller than for low-resolution datasets such as the Profiler. The gradient of the beam is also a large factor and FFF beams are the most affected. Interpolation does not have an effect.
To give an idea of when and how much the values will change, the change was performed on all the available data we have for open fields using DICOM and Profiler data and are presented in the table below. Approximately 400 datasets were evaluated.
For DICOM, only flat beams were available for analysis. For all analyses, the field ratio was 0.8, i.e. 80% field width.
Horizontal Symmetry |
Horizontal Flatness |
Vertical Symmetry |
Vertical Flatness |
|
DICOM (Flat) |
0 |
+0.02 |
+0.01 |
+0.01 |
Profiler (Overall) |
-0.20 |
+0.11 |
-0.26 |
+0.08 |
Profiler (Flat) |
-0.16 |
+0.04 |
-0.09 |
+0.01 |
Profiler (FFF) |
-0.80 |
+0.33 |
-1.26 |
+0.22 |
Profiler (Electron) |
-0.08 |
+0.30 |
-0.52 |
+0.26 |
Positive values indicate the value went up, while negative values indicate the average went down.
The data shows that for DICOM data of flat beams, the effect was negligible. This makes sense since an off-by-one error for a field several hundred pixels wide will hardly register. It is the low-resolution datasets that show a difference. The values make general sense in that symmetry generally got better and flatness got somewhat worse. The right-most element was not being evaluated and generally speaking, that’s where the beam is starting to fall off. So flatness would likely stay the same or get worse, never get better. Symmetry generally improved because now the calculation is actually being done for the points that are truly opposite it across the CAX. Previously, a given element was being compared to its opposite one element closer to the CAX than it should have been.
FFF beams change the most and this can be attributed to the larger gradients causing larger differences in the calculation for both symmetry and flatness.
I understand that this may cause some consternation because the values are suddenly changing. However, I believe this is an improvement for the better since it is now more accurate. Additionally, symmetry values are generally getting better, which is a good thing. Flatness is usually not within our control either so changes here are bothersome, but know that your energy likely hasn’t changed. As always, measure PDD for true energy determination.
Even before this issue was raised, I have been working on refactoring the profile and field analysis modules to be easier to test as well as to extend. Stay tuned.
Thanks to Stephen Terry for pointing this out. We all get better together!
Winston-Lutz¶
The WL module can now handle TIFF images. This is still provisional and may have bugs. Caution is warranted. See Using TIFF images.
Machine Logs¶
Anonymization (
anonymize()) of trajectory logs now includes the Metadata->Patient ID field in the .bin file for v4+ logs.
v 3.10.0¶
Machine Logs¶
Trajectory Log CSV files now include the Jaw positions (X1, X2, Y1, Y2) as well as couch vert and couch pitch and roll if the couch was a 6D couch.
Dynalog loading and Trajectory
to_csvcalls will now use UTF-8 encoding by default when reading/writing files.
Tomo¶
The
TomoCheesephantom can now accept density information via anroi_configparameter toanalyze. This is completely optional. See Plotting density.A new method
plot_density_curveis available. It requires that an ROI configuration has been passed per above.
Field Analysis¶
The
results_datafrom aDeviceFieldAnalysiswas throwing an error previously. It will now return aDeviceResult, which is the same as aFieldResultsave for ROI information since a device is set of profiles and does not have a ROI to speak of.
VMAT¶
Warning
The SEGMENT_X_POSITIONS_MM class attribute has been deprecated. Use the new roi_config parameter described below
which is a replacement and more.
The VMAT classes can now accept an ROI configuration dictionary to the
analyzemethod. This replaces theSEGMENT_X_POSITIONS_MMattribute. This allows the user to pass in the same details as well as ROI names. See the updated Customizing the analysis Section.The
VMATResultclass has a new attribute:named_segment_data. This is the exact same data assegment_dataexcept it is a dictionary keyed with the same names given in the roi configuration. Note that for backwards compatibilitysegment_datahas been kept.Plotting the analyzed image now renders the names of the ROIs on the image by default along with the ROI deviation value. A new parameter controls this in the
analyzemethod:show_text.
Winston-Lutz¶
Analyzing kV WL images is now a bit easier. A new parameter
open_fieldhas been added to the.analyzemethod. Setting this flag to True will set the field center to the center of the image. See the new section: kV Analysis/Imaging-only iso evaluation.Very small BBs (<2mm) may not be found. Pylinac was never meant to handle BB’s smaller than this, but it may have worked. This is now hardcoded because pylinac will add a tolerance of +/-2mm to the input BB size. For inputs of 2mm BB size, this would lead to almost any ROI being detected. This is far more likely in phantoms where there is a block + BB vs a BB in air alone. Issues finding very small BBs were resolved with this hard lower limit.
Warning
It is very unlikely but this may break your analysis if your BB is very small (<1.5mm diameter). If you are affected please reach out on the forum and I will provide you a workaround.
Winston-Lutz individual images will now show the X and Y component of the distance to the BB.
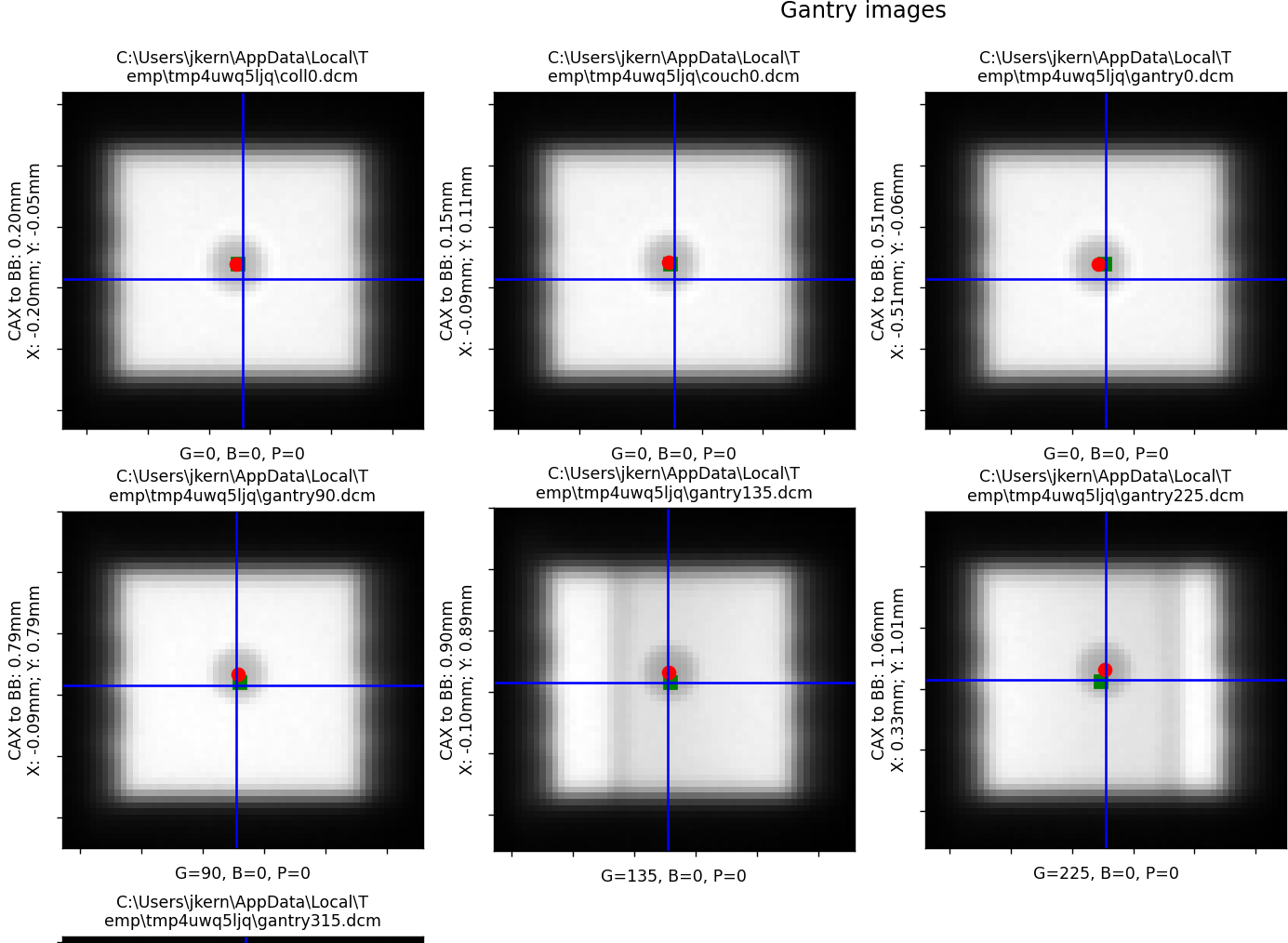
A new key has been added to the
WinstonLutzResultclass (what is returned fromresults_data()) calledkeyed_image_details. This is a dict that lets the user key off of the axes values. E.g.data['G0C90B0']will return theWinstonLutz2DResultfor that image. This is in contrast to the existingimage_detailsattribute that returns a simple list of the results. Images that are taken at the same axes values have a_{idx}appended to them. E.g. 3 images at the same position would look likeG0C0B0,G0C0B0_1, andG0C0B0_2.wl = WinstonLutz(...) wl.analyze(...) results = wl.results_data() # knowing a priori I had a G90C0B0 image g90_image_data = results.keyed_image_details["G90B0P0"] # this is in contrast to having to iterate/search over the images g90_image_data = [r.gantry_angle == 90 for r in wl.images][0].results_data()
The user can now pass the precision desired for the axes values using a new parameter:
axes_precision. This lets the user decide how to round (if at all) the axes values. E.g. a gantry at 90.1 withaxes_precision=0will get rounded to 90. This can be useful with the above if using string keys to get details from a specific image as per the example above. E.g.:# Assume an image set with G=359.9 wl = WinstonLutz(...) # default, no rounding. wl.analyze(...) wl.results_data().keyed_image_details[ "G359.9B0P0" ] # we would have to know the delivery was at 359.9 and use the appropriate key # vs wl = WinstonLutz(..., axes_precision=0) wl.analyze(...) wl.results_data().keyed_image_details[ "G0B0P0" ] # whether delivered at G=359.9 or 0.1, this will always round to the nearest integer
Note
If you consistently deliver images on the “other side of 0” you may want to set
axes_precision=0which will round to the nearest integer. I.e. if you usually do 359.9 and want it be displayed as 0 do the above. This is helpful for the example above where even if the image was at 359.9 or 89.9, settingaxes_precision=0will let you use the same consistent key, such asdata['G0C0B0']rather than having to dodata['G359.9C0B0'].Warning
Due to this new axes precision, the default sorting MAY result in a different sorting of the images. This would only affect you if doing
<wl>.images[idx]. If images are delivered on the “other side of 0” the image will bubble down to the bottom of the stack. I.e. an image delivered as G=359.9, B=0, P=0.1 will now bubble to near the bottom of the stack because the images are sorted first by gantry. Previously, the image would be rounded under the hood to be G=0, B=0, P=0. You can largely restore the prior behavior by passingaxes_precision=0
Core¶
Using
pylinac.core.profile.stretchis now deprecated and will flag a warning on usage. The only current usage in the library is forload_multipleswith the parameterstretch_each=True. This is unlikely to be used by end users and will be removed in v3.11. A new function of the same name is now available aspylinac.core.array_utils.stretch. For the normal use case where an array is to be stretched to have a new minimum and maximum, the result is the same. The use casestretch(..., fill_dtype=...)is deprecated as it is confusing and can potentially error out going from integer-like dtypes to float-like dtypes.Deprecated since version 3.11.
A new method
bit_inverthas been added to the Image classes and subclasses as well as Profile classes and subclasses. This lets the user flip the image bit-wise. This is a better alternative than the existinginvertas it takes into account the datatype. This will eventually become the default inversion method.A new method
convert_to_dtypehas been added to the Image and Profile classes and subclasses. This method will let the user pass a new numpy datatype and the array and values will be converted to that new datatype. Unlike a simple datatype casting however, this will keep the relative values to the same w/r/t the datatype max and min. E.g. an array of type uint8 has an element of value 100. Converting this to uint16 would result in a new value of 25,690 (100/255 = 0.392 = x/65535, x = 25,690). This is mostly helpful for combining images together but is a generally-helpful way of converting datatypes regardless of use case.The default value for a profile’s
normalizemethod has changed frommaxtoNone. The same is true of an Image class’snormalizemethod.maxandNonedo the same thing andmaxis still a valid argument. No change is needed by the user.Precision for axes values of
LinacDicomImages and subclasses are now more consistent and also allow the precision value to be set using a new parameter to the init call:axes_precision. Previously, any angle between 359-360 and 0-1 were considered “0”. However, this was not true for any other axes value. I.e. the above values were rounded, but no other rounding occurred. This would also only happen if using the automatic DICOM tag values. If the user passed in the axis values directly, they were used as-is. Now, the precision of all axes values can be set using the newaxes_precisionparameter. This will round the axes values to the given precision level. This will apply to both DICOM tag values as well as manually-passed values. The default behavior is to not perform any rounding. The only difference users may notice is that axes values about 359-1 are no longer rounded to 0 by default. To restore this type of behavior passaxes_precision=0which will round 359.5+ to 0 and 359.5- to 359.
v 3.9.1¶
A missing dependency in the built wheel
tabulatewas added. This only affected users who were trying to use the newWinstonLutzMultiTargetMultiFieldclass. This can also be remedied by installing the package on its own:pip install tabulate.
v 3.9.0¶
General¶
A new dependency has been added:
tabulate. This is a Python-only library used for the new multi-target WL module. It is also a dependency ofpandas, which will likely be a dependency of pylinac in the future.
CatPhan¶
ROI details have been added to the
CTP515Resultclass.Passing
deltatosave_analyzed_subimagewould fail because the parameter was not being passed. This is now fixed.
Cheese¶
A new module for “cheese” phantoms has been created. Only one routine currently exists: the
TomoCheese, but more will be added later. Documentation for this new phantom can be found here: “Cheese” Phantoms.
Winston-Lutz¶
Multi-Target, Multi-Field Winston-Lutz is now available. This means phantoms such as the SNC MultiMet can be analyzed. The algorithm is generalized however, and any reasonable configuration of BBs can be analyzed, meaning custom phantoms and new commercial phantoms are easy to make. Read the new section here.
BBs with low density compared to surrounding material can now be analyzed via a new parameter
low_density_bb. See theanalyze()method.
Image Generator¶
The
generate_winstonlutz()utility script now accepts afield_alphaandbb_alphaparameter to set each item respectively.
Bug Fixes¶
Certain XIM images were failing to render. This has been fixed.
v 3.8.2¶
Using
use_filenameswithaxis_mappingwhen instantiating Winston-Lutz would not respect theuse_filenamesflag. Now,use_filenamestakes precedent. Normally, these should not be used together since they are both trying to set the axis values.
v 3.8.1¶
The SNC phantoms (kV, MV, MV 12510) have had their ROI localization algorithms adjusted slightly. These phantoms are commonly used with the acrylic jig. That jig is very dense and often causes issues detecting the phantom separate from the phantom itself. This fix should remove the effect of the acrylic jig and allow any jig to be used, assuming the central ROI area is not occluded.
Winston-Lutz axis-specific RMS calculations (“Maximum <Gantry | Collimator | Couch> RMS deviation”) from the
resultsandresults_datamethod calls were potentially erroneous if the maximum error was in a “Reference” image (gantry=coll=couch=0). Users are urged to upgrade if using these outputs. Note that the Maximum/Median/Mean 2D CAX->BB distances are unaffected.
v 3.8.0¶
General¶
.ximfiles are now able to be opened. These are Varian-specific images usually taken during MPC or in service mode. Currently, it is not natively integrated into other analyses (e.g. analyzing a .xim picket-fence viaPicketFence(...)), but depending on the usage it will have more mainstream support in the other modules. However, this will allow the user to export to other, common file formats like png, jpeg, and tiff as well as access the properties of the .xim image such as acquisition mode, MLC positions, etc. Read about it here: XIM images.
Image Generator¶
The image generator module has had tests added to increase robustness as well as docstrings for the parameters.
The
RandomNoiseLayerhas been adjusted to provide noise irrespective of the signal. Previously, the noise was dependent on the intensity of the pixel. To be consistent with the intention of applying dark current, the layer now adds noise consistently across the image. The default sigma value has been adjusted to be roughly the same as before.
Picket Fence¶
The PDF generated when the orientation was up/down would sometimes occlude the text on the report. The image placement has been adjusted.
Winston Lutz¶
The
results_data()for a normal WL analysis now include the details of each image as well. I.e. EachWinstonLutzResultcontains NWinstonLutz2DResult, one for each image, under theimage_detailskey.
CBCT¶
The MTF returned in
results_datanow includes 10-90 in steps of 10. Previously, only the 80, 50, and 30% were reported.
v 3.7.2¶
Field Analysis¶
Performing a field analysis on a very small field (a few mm) would error out. To get around this, pass a larger
slope_exclusion_ratiotoanalyze().
v 3.7.1¶
Planar Imaging¶
The SNC MV 12510 ROIs were slightly downscaled. This caused an issue in contrast and CNR calculation being lower than reality by ~20%. It was introduced in v3.6. Users are encouraged to upgrade if using this specific phantom analysis.
v 3.7.0¶
General¶
Logos can now be passed to any
publish_pdfmethod to insert a custom logo (e.g. an institution logo). The size of the logo as it appears on the PDF is fixed.
Picket Fence¶
The
max_error_picketandmax_error_leafhave been added to the results returned from<pf>.results_data().Elekta MLC options have been added to the
MLCenum.
Planar Imaging¶
Inversion detection for the Leeds and PTW EPID QC phantoms have been improved.
Warning
If you are passing
invert=Trueto the analyze method for these phantoms double check the outcome. There is a good chance that parameter can be removed.An angle check has been added to the SNC kV phantom. Previously, the angle was hardcoded at 135 degrees per the manufacturer recommendation. It now checks the detected angle. If the value is 135+/-5 degrees the detected angle is passed, otherwise an error is thrown.
CBCT¶
The phantom center detection was refactored. This was because the RadMachine jig was touching the CatPhan and causing detection issues on a handful of slices. Unfortunately, these few handful of slices were important to the detection algorithm as they occurred around the HU linearity module for the 604. The phantom center of each slice along the Z axis (in/out) is now detected by fitting a 1D polynomial for all the slices where the phantom is detected. I.e.
x, y = f(z). This removes some of the error associated with having something touching the phantom for just a few slices. E.g. a clinic was using BBs on the side of their Catphan for alignment which was causing issues. Situations like these are more likely to be recovered from.Note
This change is internal and should not cause issues; all tests passed without modification but there is a small possibility a dataset with some kind of interference will now analyze and cause detection issues.
v 3.6.3¶
CBCT¶
Cropping a catphan dataset before analysis would result in an analysis failure.
Datasets that had a deep-curve couch very close to the phantom (e.g. head cradles) would fail.
v 3.6.2¶
CBCT¶
The phantom center detection was refactored. This was because the RadMachine jig was touching the CatPhan and causing detection issues on a handful of slices. Unfortunately, these few handful of slices were important to the detection algorithm as they occurred around the HU linearity module for the 604. The phantom center of each slice along the Z axis (in/out) is now detected by fitting a 1D polynomial for all the slices where the phantom is detected. I.e.
x, y = f(z). This removes some of the error associated with having something touching the phantom for just a few slices. E.g. a clinic was using BBs on the side of their Catphan for alignment which was causing issues. Situations like these are more likely to be recovered from.Note
This change is internal and should not cause issues; all tests passed without modification but there is a small possibility a dataset with some kind of interference will now analyze and cause detection issues.
v 3.6.1¶
Fixed a bug with the SNC MV phantom analysis where the ROI scaling for the entire phantom was slightly over-sized.
v 3.6.0¶
Planar Imaging¶
Planar analyses had a discrepancy in the number of low-contrast ROIs “seen” in the plot vs what was given in the numerical results. This is because the numeric results were still using the older method of contrast analysis, which does not take into account the ROI size. The plot uses the newer method of Visibility. The quantitative results have been changed to use the visibility.
Warning
Your detected ROIs may be different moving forward, although the visibility default value in the
analyze()method was chosen to be as close as possible to the existing contrast results, meaning that the ROIs should be similar out of the gate. If you’d like to still use the older metric it is still available:num_rois_simple_contrast = sum( roi.passed for roi in my_planar_phantom.low_contrast_rois )
Picket Fence¶
The
max_error_leafproperty will now return an int, where previously it returned a single-element list for classic/combined analysis. I.e. doing<pf>.max_error_leafused to return something like[42]but now returns42. The signature type has also been updated to reflect this. This change allows the user to do this:<pf>.plot_leaf_profile(leaf=<pf>.max_error_leaf, picket=<pf>.max_error_picket). Previously, this would fail because themax_error_leafwas a list and the user would have to do...leaf=<pf>.max_error_leaf[0]....Note
Users that perform “separate” analysis are unaffected (
.analyse(... separate_leaves=True).
Winston-Lutz¶
The BB-finding algorithm has been hardened and can now find the BB even in the presence of artifacts such as the couch. This most often applies when very large fields are used. A side effect is that the BB-finding algorithm is also now faster and reduces analysis time up to 50%.
The machine coordinate system/scale can now be given as a parameter. This will affect the BB shift vector and shift instructions. The default scale is IEC61217, which was the implicit default previously and is thus backwards-consistent. A small section has been added here: Passing a coordinate system.
Due to the above change, there is no need for the
couch_angle_varian_scaleproperty of theWinstonLutz2Dclass. It has been removed to reduce confusion. Use the new feature above if you had been using/overriding this property.A bug was fixed where repeating analysis would give different results. This was because the image pre-processing was being performed each time
.analyze()was called. This only applies if you perform.analyze()more than once on the same instance.
Catphan¶
The Catphan 600 MTF algorithm had a bug of not using the correct “windows” of peaks/valleys when finding the MTF. Each CatPhan model’s high-resolution pairs are at slightly different angles. The 600 was inadvertently using the 504’s window positions. This has been updated to use the correct windows. The problem can be visualized below, where the red lines show each MTF resolution window previously, vs the green which is the updated window. The result is that MTF will now be lower than previously because the old windows were sometimes including a peak of the previous line pair, causing the apparent MTF value to be higher than it really was.
Warning
MTF values for the CatPhan 600 will now be ~15% lower than previously due to this bug fix.
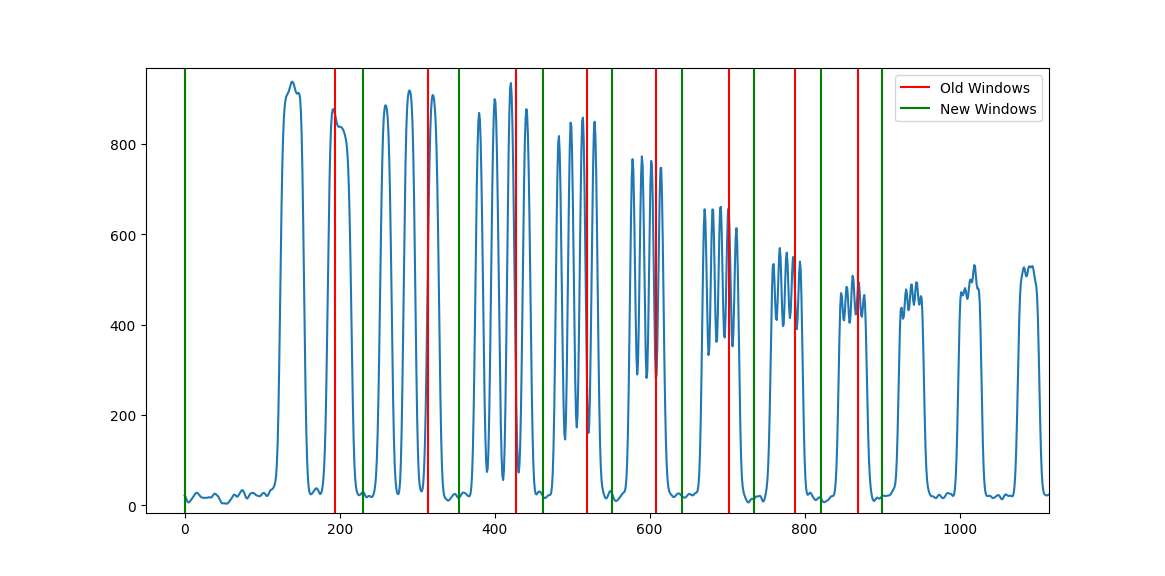
Field Analysis¶
A visual bug was fixed with the blue ROI display. The horizontal ROI was being offset slightly based on the vertical width. This only applied when the width of the horizontal and vertical parameters were different and is completely visual. No quantitative results are affected.
The statistics from the central area within the horizontal and vertical windows is now reported. I.e. the stats from the pixel values within the overlap of vertical window and horizontal window are now available like so:
fa = FieldAnalysis(...) fa.analyze(...) results = fa.results_data() results.central_roi_max results.central_roi_mean ...
The stats are also available directly from the FieldAnalysis instance:
fa = FieldAnalysis(...) fa.analyze(...) fa.central_roi.mean fa.central_roi.max ...
If the width is 0 for both parameters a 2x2 matrix is sampled around the central pixel.
Core¶
The
RectangleROIclass now has additional statistical results available computed from the pixel array:.mean,.std,.min,.max.
v 3.5.0¶
Planar Imaging¶
Older SNC MV phantoms (observed as model #1251000) can now be analyzed with the new
SNCMV12510. They have a slightly different size and ROI locations but appears to be functionally the same.The IBA Primus A phantom is now supported.
Planar image analyses now take into account the image SAD; previously this was assumed to always be 1000mm. This only affects users with non-standard SADs such as proton gantries. Linac-based users should see no difference.
Most planar phantoms will now show an “x” marker on the analyzed image showing the detected center of the phantom. This can help in evaluating the algorithm’s accuracy in phantom detection.
Two methods,
window_floorandwindow_ceiling, were added to the image analysis classes. This lets the user define the min and max values of display for plotting the image. These are convenience functions only and currently only affect the Primus phantom, but will likely be adopted for the other phantoms.
Core¶
A source-to-axis
sadproperty was added to theDicomImageclass. This property looks up the “RadiationMachineSAD” tag. This was added because non-1000mm SADs are being encountered.The
dpmmproperty now takes into account the SAD (see above). Previously, the SAD was assumed to be 1000mm. For Linac users there will be no visible change.
Bug Fixes¶
The PDFs from planar imaging analyses would have the text collapsed to one line. This has been fixed.
The planar imaging module was starting to use scikit-image attributes that were introduced in 0.19 inadvertently. This has been fixed. For previous versions, update scikit-image to v0.19 or higher.
v 3.4.0¶
Picket Fence¶
There is now a
skew()method, returning the skew of each picket.
Planar Imaging¶
A new class for analyzing older Leeds phantoms that have a blue label on the back (vs the red ring) has been added:
LeedsTORBlue
Winston-Lutz¶
The
cax2bb_distance()method can now acceptmeanfor the metric.The
cax2epid_distance()method can now acceptmeanfor the metric.The
results_data()now includes the mean CAX->BB distance and mean CAX->EPID distance.
CT¶
The
CatPhan600detection has changed to use the bottom Air ROI and the Teflon ROI (just to the right of bottom air ROI). This is because the top air ROI can sometimes (and purposefully) contains a water vial. When inserted, the water vial makes angle detection untenable using this ROI. The result should be <0.5 degrees difference from previous versions, however, it was never 0. The only result this should affect (other than the angle) is the very small ROI low-contrast detection values, as it was found that even with a few tenths of degrees, a single pixel or two would be included or excluded compared to the previous algorithm. This is really a reflection of the sensitivity of the noise, which should likely use a global noise value instead of the local noise.Related to above, the same class now will have an extra ROI “Vial” with an expected value of 0. However, if the detected ROI is closer in value to air than water, the ROI will not be evaluated. This gives backwards-compatibility with existing scans that don’t use the vial. I.e. if you don’t use the water vial nothing should be different.
v 3.3.0¶
Core¶
1D gamma evaluation between two profiles can now be performed via the new
gamma()function.Resampling of
SingleProfilecan now be done with theresample()function. This allows the user to resample a profile after it’s already been created to achieve a specific interpolation resolution.
Field Analysis¶
The
DeviceFieldAnalysisclass has been removed. Only the SNC Profiler was supported and even then it didn’t work very well. Further, RadMachine is utilizing profile/file parsing that will be brought to pylinac. This new generalized scan parsing will eventually restore similar behavior, but for now it is deprecated. Sorry ☹
Planar Imaging¶
The SNC FSQA light/rad phantom is now able to be analyzed. Docs can be found here: SNC FSQA.
Bug Fixes¶
#1705 - PDDx for measurements with no lead and PDD < 75 would calculate using the interim equation of 1.267*pdd - 20. This should return the PDD if the PDD<75. This will result in ~0.3% difference for 10MV with PDD just under 75. Depending on the chamber you’re using, this could result in a difference of kQ by ~0.0005.
The planar imaging detection routines have slightly improved robustness. This was caused by using scikit-image’s
major_axis_lengthproperty, which is somewhat more finicky than other properties. The detection now uses thearea_bboxproperty which appears to curb some edge-case phantom analyses. This should not affect results for images that are already detected properly.Linear and Spline interpolation for
SingleProfilecontained an error in how it was interpolating data (it wasn’t) at the very edges. The problem is that if we upsample, the left and right ends are not equally sampled. E.g. upsampling a 3-pixel array (0, 1, 2) by 10 normally results in ~20 elements. You interpolate between 0 and 1, and 1 and 2. The first issue is that you do not have a simple X proportion of elements (3 * 10 = 30 but we get 20). Additionally, if these are pixels they have a finite, physical size and technically those values are at the center of the pixels. Thus, you actually need to sample beyond the left and right edges. In the above case you’d really need to sample from approximately -0.5 to 2.5 to get ~10 pixels for each original pixel. We also need to offset the x-values to be back to 0 again from -0.5. We solve this by offsetting the new x-values by a proportion of the sampling ratio. A ratio of 1 (identical sampling) should not have any offset and return the same values. As the ratio goes up, we approach the limit of 0.5 pixels. This follows a proportional relationship with the ratio. The end result actually does not change much in the way of measurement results as nearly every previously-existing tests passed. 2 out of ~50 field analysis tests had a slightly different penumbra measurement and 1 had a slightly changed vert symmetry.
v 3.2.0¶
General¶
The codebase as been blackened. This does not affect functionality but will change code line numbers when comparing to previous versions.
All internal imports have been converted to relative imports. This does not change functionality but does mean that the pylinac repo can now be easily forked and included as a package in RadMachine. This would typically be done to use a pinned version as the embedded pylinac in RadMachine is updated regularly.
Pylinac has dropped support for Python 3.6, following the security support timetable. 3.7 support will drop in the next version after June 2023.
Planar Imaging¶
The IMT L-Rad light/rad phantom is now able to be analyzed. It is part of the planar imaging module. Docs are here.
The SI QCkV phantom was accidentally analyzing the reference/background ROI. This resulted in a contrast of 0 for the first ROI all the time. This has been removed from the results. Calculations using the average contrast will be affected. Existing ROI analysis values are not affected, but will be off by one if accessing the roi directly. I.e. “roi 3” is now “roi 2”, etc as the reference ROI was originally “roi 1”.
CT¶
The Quart phantom can now be analyzed. Docs are here.
The ACR CT and ACR MRI Large phantom can now be analyzed. These should be considered experimental and subject to breaking changes in future versions until substantial data/tests can be had. Docs are here.
The catphan and quart classes have a new attribute:
hu_origin_slice_variance. This allows users to override the acceptable variance used to find the HU linearity module. Existing functionality is not changed.
Winston-Lutz¶
Axis data can now be passed in as a dictionary. This is mostly for Elekta users. This is an alternative to renaming files. See the updated section on passing in data.
The
ImageManagerclass has been removed. The functionality has been absorbed into the existing classes.
v 3.1.0¶
General¶
For the picket fence, field analysis, and planar imaging modules, image keyword args can now be passed on instantiation. This is helpful for images that don’t have even basic tags like DPI/DPMM or SID. The keyword args that can be passed are those consumed by
load().from pylinac import PicketFence path = ... # very sad image that has no DICOM tags for DPI or SID pf = PicketFence(path, image_kwargs={"dpi": 184, "sid": 1500}) pf.analyze() ...
Matplotlib keyword args can now be passed to most modules that save a figure, allowing the user to specify the figure size and other parameters
from pylinac import LeedsTOR leeds = LeedsTOR.from_demo_image() leeds.analyze() leeds.plot_analyzed_image( ..., figsize=(10, 10) ) # figsize is passed to matplotlib to generate a figure of said size
Pylinac is now compatible with scikit-image 0.19
Picket Fence¶
Individual leaf errors (on each side of the picket) can now be analyzed. New parameters were introduced to add this and related information needed to compute this. For backwards-compatibility this is set to False. See the picket fence documentation and
analyze()parameter descriptions, specifically theseparate_leavesandnominal_gap_mmparameters.Algorithm benchmarking has been added to the PF docs.
Planar Imaging¶
The Standard Imaging FC-2 light/rad phantom is now able to be analyzed.
The Las Vegas contrast analysis has been reverted to pre-3.0 behavior. This is because there is no reference position like there is for other phantoms. Mistakenly, the “reference” was set to the first ROI, but because visibility is dependent on both ROI size and contrast for Las Vegas, the background ROIs outside the milled disc areas have been restored.
Plots can now be separated. Use
.plot_analyzed_image(... split_plots=True). This will now show multiple matplotlib plots.You may save analyzed images to individual files. I.e. when splitting per above each plot will be saved to a separate file. See
save_analyzed_image(). This will return the filenames on disk.Finally, you may save split plots to stream using
to_streams. This will return a dictionary of the plot name (image, low contrast, …) and stream.
Field Analysis¶
The plotting behavior described above for planar imaging is also true now for field analysis.
Passing a string for centering, interpolation, edge and normalization methods is now an option. E.g.
<field analysis instance>.analyze(..., centering='manual', ...).
CBCT¶
The catphan module can now accept a list of paths on instantiation. E.g.
Catphan504([path1, path2, path3, ...]).
Winston-Lutz¶
The
plot_summary()method now allows you to pass a figure size.With the above,
save_summary()also allows you pass the figure size.
Bug Fixes¶
#1464 - Off-center CBCT could give faulty slice thickness numbers. The row/col were inverted for the sampling, meaning the left ROI was really sampling the top ROI and vic versa. For an on-center catphan, this would not change the results. Results appear to only have changed if the catphan was 5+ mm off-center. The change of outcome for offsets large than this are indeterminate but likely you weren’t getting good results to begin with under that scenario, so it should only improve.
#405 - The picket fence
results()were reporting the wrong picket for the maximum error. It was selecting from a wrongly-ordered list, instead giving the picket with the least error. Note that the maximum error value was not incorrect, only the reported picket.PDF generation for field analysis with a device (i.e. SNC Profiler data) would fail as there was no true image. The PDF generation simply skips the image plotting for devices now.
#416 - The CBCT docs now correctly state that the slice thickness is based on all the wire profiles, not just the longest two.
#408 - The Dynalog isoplane correction factor was changed from 1.99614 to 1.96078 to match Varian documentation. This should have a difference of <0.3% of positioning error and should not affect gamma (since the errors canceled out) but would affect comparison to a TPS fluence.
v 3.0.0¶
Warning
Version 3.0 contains numerous breaking changes (hence the increment). Review the changelog before upgrading.
General¶
A new method,
results_datahas been added to most modules (excluding calibration and log analyzer). This is complementary toresults.results_datawill return a dataclass or dictionary, which includes pretty much everything inresultsas well as metadata (e.g. pylinac version). This dictionary will be useful for APIs and referencing certain information that will be more stable across versions 🤞. Thanks to @crcrewso for the suggestion.Nearly all major modules can now handle file objects and streams (Dynalogs cannot yet). These may be passed as would a disk file path.
with open("mystarshot.dcm", "rb") as f: star = Starshot(f) ...
Enums have been added in numerous places to mostly replace string options. E.g. for picket fence instead of specifying “up-down” as the orientation literally, the user now has the option to pass an Enum:
from pylinac.picketfence import PicketFence, Orientation pf = PicketFence(...) pf.analyze(..., orientation=Orientation.UP_DOWN) # specify the orientation via an Enum
The advantage here is two-fold: 1) introspection/autocompletion using your IDE vs remembering/looking up documentation, 2) easier to generate documentation as now we can point to a class with the options. Note however that string options are still available for backwards compatibility.
pf = PicketFence(...) pf.analyze( ..., orientation="Up-Down" ) # specify the orientation via a string. Works the same as above
Assuming you’d like to use the string version instead of using enums all over, how do you know the options? Go to the auto-generated documentation of the enum! =) E.g.
Orientation.Note
Relying on your IDE is a good idea. A smart one can warn you of incompatible data types.
The github repo has been “minified” by removing excess demo files and also removing the basic test files. These files are now cloud-hosted and downloaded as needed. This makes
git clonesignificantly faster since the repo size has been reduced from ~1.6GB to ~60MB. Note that this does not affect the pip package since that package already had most of this excess data removed.Image inversion detection has changed slightly. Some images have proper tags such as rescale slope and intercept. If they do have the tags, they are applied and no inversion is applied. If they do not have the tags, an inversion is then applied. Previously, the tags were applied if they were there, and nothing if not and inversion was ALWAYS applied. This should result in better inversion defaults for images from different machines/platforms and fewer
invert=Trueadditions. See Images.A
CONTRASTenum has been added that can be used for low-contrast analysis of planar images and CBCT images. See Contrast.from pylinac.core.roi import Contrast leeds = LeedsTOR(...) leeds.analyze(..., low_contrast_method=Contrast.WEBER) ... ct = CatPhan504(...) ct.analyze(..., contrast_method=Contrast.MICHELSON) ...
The algorithm for low contrast contrast constant detection has changed slightly. See Visibility. This means the # of detected low-contrast ROIs may change for cbct. You may pass in a contrast technique per above and also a visibility threshold. See the
.analyzemethod of the respective class.The contrast-to-noise property of the LowContrastDiskROI now uses contrast/stdev, where contrast is defined/chosen per above.
Several LowContrastDiskROI properties have been deprecated such as
contrast_constant. Usevisibilityinstead. The old properties still work but come with a deprecation warning and will be removed in a future release.#270 Pylinac had a memory leak that was apparent when running on a server. This was caused by old instances being held in memory from and incorrect usage of the
lru_cache. This has been fixed.Documentation about topics has been added.
Documentation benchmarking several algorithms has been added. See the “Benchmarking the Algorithm” section for vmat, winston-lutz, and starshot modules. Picket fence will come soon.
Note
Upgrade Hints
Besides the above notes and any module-specific steps, due to the modified method of loading images and inversion, other downstream modules may be affected.
This means that some images that needed invert=True before may not need it, and some images that previously worked
may need an invert=True. So generally, if the image fails when it passed with previous versions, try adding/removing forced inversion
first. This should only be an issue for older images. Images generated on new linac platforms should be handled just fine.
Dependencies¶
A new dependency has been added: cached_property.
Field Analysis (previously Flatness/Symmetry)¶
Danger
This release introduced numerous breaking changes to this module. Existing code will break.
Two classes are now offered:
FieldAnalysisandDeviceFieldAnalysis.Many, many options were added to the
analyze()method. See below and the documentation page for all the details.The
flatsymmodule has been renamed tofield_analysisto reflect the generalized nature of the module. Many thanks to Alan Chamberlain (@alanphys) for suggesting and doing the initial implementation for this. This also introduced some early support for NCS-33 , which gives guidance on FFF beams.From the above report, a “top” position as well as field slope values are calculated for FFF beams. See FFF fields.
The new module can handle files from devices, specifically the SNC Profiler.
Extensibility was greatly enhanced. Users can now easily add their own custom analysis routines to the module. See Creating & Using Custom Protocols.
New options for Centering, Normalization, Edge detection, and Interpolation were introduced. Each of these can be granularly controlled.
VMAT¶
Leveraging the new profile module, the field edge detection has been improved and can detect “wide-gap” or overlapping ROIs more robustly.
Calibration¶
#353 The bounds for most functions/methods have been converted to constants. This lets users override the default values should they wish it.
Winston-Lutz¶
#366 #333 The analysis will fail if the BB is not detected within 20mm of the center of the field. This should help artifacts from being detected.
The Winston-Lutz analysis has added an
.analyzeroutine, just like all other major modules.#358 The user can now pass in an expected BB size. This will help analyses with smaller or very large BBs.
The
WLImageclass has been renamed toWinstonLutz2D. This is to clarify usage as now documentation has been expanded to show using WL with a single image.
Note
Upgrade Hints
Replace any uses of axis constants (
GANTRY,COLLIMATOR, etc) with the enum version:Axis.GANTRY, …Add a
<instance>.analyze(...)call to eachWinstonLutzinstantiation.Set the BB size if needed. The algorithm has a default of 5mm and is relatively forgiving (+/-2mm), but for very small BBs you should set it lower than the default of 5mm. E.g.
.analyze(bb_size_mm=3)If using
WLImage, rename toWinstonLutz2D. Add.analyze()calls as well as appropriate.
I/O¶
An SNC Profiler file parser has been added:
pylinac.core.io.SNCProfiler. This can be used standalone, but since the data is not encoded to begin with it’s really about handling it as a tool for other modules. Currently, this is being used in the Field Analysis module.from pylinac.core.io import SNCProfiler snc = SNCProfiler("path/to/data.prs") snc.data # ndarray x, y, pos, neg = snc.to_profiles() # returns SingleProfiles
Planar Imaging¶
Sun Nuclear kV and MV phantoms have been added to the arsenal.
The PTW EPID QC phantom has been added to the arsenal.
The Standard Imaging QC-kV1 phantom has been added to the arsenal.
#339 The user can now pass an SSD value for their phantoms. The default is 1000mm, but if you set it on your panel you can pass something like 1400mm.
The phantom-finding algorithm has been refactored to be more extensible. This does not affect normal users, but reduces the amount of duplicate code. It also makes adding new phantoms easier.
Generally speaking, the phantoms should all be roughly centered along the CAX. Previously, the phantom could be offset from the CAX. Due to general difficulty in finding the phantom reliably for the majority of clinics, I am enforcing this as a restriction. This shouldn’t affect too many people but should make the ROI-finding algorithm better.
The low contrast background ROI (i.e. the base level of contrast) has been adjusted for some phantoms (QC-3 and Doselab). Previously, it could either be in a “dark” region, meaning a high-attenuation area, or a “light” region, meaning a low-attenuation area. This has been standardized for all phantoms to be the “light” region. A new doc page for contrast has been added to the online documentation.
3 more high-contrast ROIs have been added to the LeedsTOR to help get rMTFs below 50%.
The SI QC-3 analysis will now handle both typical orientations (gantry 0 and 90), where the “1” is pointing toward the gantry. This produces two different angles. The phantom should still be angled at 45 degrees from a cardinal angle.
Note
Upgrade Hints
If you have defined any custom phantoms, read the new documentation: Creating a custom phantom. Your existing code will likely NOT break but the new format is much easier for extensibility.
Evaluate the new contrast values versus your existing ones for the QC3 and Doselab phantoms. Moving forward, the above definition of contrast ROI-picking will be used.
For the LeedsTOR, check the MTF of an existing image. Since adding more high-contrast ROIs, the rMTF may change if you were using a value below the lowest detected value. You do/will get warnings about being below the minimum MTF if you already do so.
Picket Fence¶
Overall, most code shouldn’t need to change from v2.5. From v2.4 or below, the way MLCs are passed and used has changed.
Wide-gap tests should now work better than before. However, please read the Acquiring good images section.
The
mlcparameter of thePicketFenceconstructor has been changed to use an Enum orMLCArrangement:MLC. See the Customizing MLCs section for more.A
crop_mmparameter has been added to thePicketFenceconstructor. This is for cropping the edges of images. The primary cause of issues with the PF module is dirty/noisy/dead edges.The
orientationparameter of theanalyzemethod has been changed to use an Enum or str:Orientation.A
required_prominenceparameter has been added toanalyze. This is to prevent multiple peaks detection for wide-gap images.A
fwxmparameter has been added toanalyze. This is to allow the user to set the FWXM height to use for the MLC kiss profile.A
results_datamethod has been added. See General above.The colored rectangular overlay has been reduced in size slightly.
CBCT¶
A
contrastparameter was added to analyze. This uses an Enum and has 3 options; see Low contrast.A
visibility_thresholdparameter was added and is a replacement forcnr_threshold. See the General section and Visibility. Compared tocnr_threshold, the default value will give approximately the same results for # of low-contrast ROIs “seen”. About 30% of the test datasets had a different # detected, but the detected vs expected number were either too high or too low, so there was no single value to perfectly replace the defaultcnr_thresholdvalue.With the above, the contrast calculations have been standardized. Compared to previously, the contrast and contrast-to-noise now use the same equation for contrast. Previously, contrast was using the Michelson equation and contrast-to-noise was using the Weber definition. Now, contrast is always calculated with the definition given during instantiation.
ROI colors for low contrast ROIs that are “seen” have changed from blue to green to match other modules.
Note
Upgrade Hints
Change/check the contrast method of .analyze().
Change/check the visibility threshold of .analyze().
Verify the # of low contrast ROIs “seen”.
Machine logs¶
#161 Trajectory logs v4.0 are now supported
v 2.5.0¶
Warning
There appears to be an issue with reading TIFF images on Windows with libtiff=4.1.0. If you experience TIFF header errors, downgrade libtiff to <4.1.
General¶
This release adds utility functions to the image generator module and also a change in configuration of the picket fence module, allowing users to create their own MLC configurations.
Dependencies¶
py-linqhas been added as a dependency. It’s pure python so it will not add secondary dependencies.
Picket Fence¶
MLC configuration has changed from being empirical to a priori, meaning that leaves are no longer determined, but passed in via configuration. This allows users to configure their own custom MLCs arrangements. See Customizing MLCs.
Linked with the above, the
is_hdmlcparameter is deprecated and users should now use themlcparameter in the constructor.Also due to above, new parameters have been added to the
analyzemethod. Please see the documentation for more info.The colored overlay is now broken up into the individual leaf kisses rather than one line.
Several internal classes were removed or overhauled. This should not affect you if you’re just using the basic routines like analyze().
Settingsno longer exists,MLCMeasis nowMLCValue.PicketManagerno longer exists.
VMAT¶
The ROI segment size can now be specified in
analyze. This is discussed in the new section Customizing the analysis.
Image generator¶
In the previous release, a new image generator module was introduced. This release adds utility scripts for easily creating Winston-Lutz and picket fence image sets. See the Helpers section of the generator documentation.
v 2.4.0¶
General¶
Thanks to several contributors for making pull requests in this release!
A new image generator module has been added. This module can generate custom test images easily: Image Generator.
The core peak-finding functionality used in several modules was refactored to use scipy’s implementation. When pylinac was built, such a function did not exist. Now that it does, the custom code has been removed (yay!). The major difference between this implementation and pylinac’s is the use of “prominence”, which is a concept I had never heard of. The resulting peak-finding functionality is the same for max-value peak-finding. For FWXM peak finding, this can have small differences. The biggest differences would be for profiles that have a very asymmetric “floor”. I.e. if one valley on one side of the peak has a very different value than the other side then a difference would be detected. Fortunately, this is a very rare scenario.
Documentation plots have been updated to be generated on-the-fly. This will result in better agreement with documentation plots vs. what people experience. Previously, some old figures were used that did not match the functionality.
The GUI function was removed from the pylinac init file. This was causing issues when deploying to Heroku as calls to tkinter caused failures. The GUI should be called from the submodule now:
# old import pylinac pylinac.gui() # new from pylinac.py_gui import gui gui()
Dependencies¶
Two requirements have been bumped: scipy>=1.1 and scikit-image>=0.17.
CT Module¶
If you do not perform any advanced functionality, no changes are noteworthy.
The CT module has been reworked to be far more extensible to adjust individual component modules as desired. Previously, only the offset of the modules was easily adjustable. To edit individual modules the user would have to edit the source code directly. Now, the user can subclass individual modules, overload attributes as desired and pass those to the parent CatPhan class. A new tutorial section has been added to the documentation showing examples of this functionality.
The CTP404 and 528 modules have been refactored into CatPhan-specific classes for easier overloading by appending “CP<model>”. E.g. CTP404CP503.
CTP modules had an inconsistent naming scheme for rois. E.g. CTP404 had
hu_roisandbg_hu_roiswhile CTP515 hadinner_bg_roisandrois. This has been standardized (mostly) intoroisfor all modules and, where applicable,background_rois. Some modules still have more relevant attrs, e.g.thickness_roisfor CTP404, but they all have haverois.Due to the above refactor, you may notice small differences in the contrast constant value and thus the ROIs “seen”.
HU differences are now signed. Previously the absolute value of the difference was taken.
HU nominal values have been adjusted to be the mean of the range listed in the CatPhan manuals. The changes are as follows: Air: N/A (this is because most systems have a lower limit of -1000), PMP: -200 -> -196, LDPE: -100 -> -104, Poly: -35 -> -47, Acrylic 120 -> 115, Delrin: 340 -> 365, Teflon: 990 -> 1000, Bone (20%): 240 -> 237, Bone (50%): N/A.
Flatness & Symmetry¶
The flatness & symmetry module has been updated to allow for profiles of a select width to be analyzed rather than a single pixel profile.
A
filterparameter has been added to the constructor. This filter will apply a median filter of pixel size x.Due to the new peak-finding function, flatness and symmetry values may be slightly different. In testing, if a filter was not used the values could change by up to 0.3%. However, when a filter was applied the difference was negligible.
Two new keyword parameters were added to analyze:
vert_widthandhoriz_width. You can read about their usage in theanalyzedocumentation.The
plot()method was renamed toplot_analyzed_image()to match the rest of the modules.
Watcher¶
The watcher script has been officially deprecated for now (it was broken for a long time anyway). A better overall solution is to use something like QATrack+ anyway =).
Bug Fixes¶
#325 The Leeds angle detection should be more robust when the phantom angle is very close to 0.
#313 The catphan CTP486 module had an inverted top and bottom ROI assignment.
#305 The Leeds
invertparameter was not being respected.#303 Un-inverted WL image analysis would give an error.
#290 Catphan HU linearity differences are now signed.
#301 Loading starshots and picket fences from multiple images has been fixed.
#199 Printing Picket Fence PDFs with a log has been fixed.
v 2.3.2¶
Bug Fixes¶
#285 The SI QC-3 module was incorrectly failing when the phantom was at 140cm due to a faulty mag factor.
v 2.3.1¶
Bug Fixes¶
#281 The ct module had a wrong usage of the new MTF module that caused a break.
v 2.3.0¶
General¶
The dependencies have been updated. Scikit-image min version is now 0.13 from 0.12. There is also no upper pin on numpy or scikit-image.
The planar imaging module was overhauled.
An MTF core module was introduced to refactor and standardize the MTF calculations performed across pylinac.
The Winston-Lutz 2D and 3D algorithms were improved.
Winston Lutz¶
The coordinate space definition has changed to be compatible with IEC 61217. This affects how to understand the 3D shift vector. The
bb_shift_instructionshave been modified accordingly to still give colloquial instructions correctly (i.e. “Left 0.3mm”).The WL module received an internal overhaul with respect to the 3D shift algorithm (i.e. the BB shift vector/instructions). The 3D algorithm was reimplemented according to D Low’s 1994 paper. Generally speaking, the results are more stable across multiple datasets, however, you may see individual differences of up to 0.3mm.
Due to above, the
bb_<axis>_offsetandepid_<axis>_offsetproperties have been removed.Two new image categorizations have been added:
GB ComboandGBP Combo. These represent a gantry/collimator combination image with the couch at 0 and gantry/collimator/couch image where all axes are rotated.GBP Combois a replacement forALL. This change should only affect users who explicitly call methods that ask for the image set like.axis_rms_deviation,.plot_axis_images, etc.A new property has been added:
.gantry_coll_iso_sizewhich calculates the isocenter size using both gantry and collimator images.A new property has been added to individual images:
.couch_angle_varian_scale. This conversion is needed to go from IEC 61217 to “Varian” scale for proper 3D shift vector calculation per the 3D algorithm change. Users likely wouldn’t need this, but it’s there.The 2D CAX->BB vector is improved slightly (#268). Thanks to @brjdenis and @SimonBiggs for bringing this to my attention and helping out.
Planar Imaging¶
The Doselab MC2 (MV & kV) phantom has been added to the planar imaging module.
The planar imaging module has been overhauled. The automatic detection algorithms have been spotty with no easy way of correcting the inputs. Further, each phantom had a few subtle differences making them just different enough to be annoying.
To this end, the phantom classes have been refactored to consistently use a base class. This means all main methods behave the same and give a standardized output.
Creating new custom phantom classes is now very easy. A new section of the planar imaging documentation has been added as a guide.
A
resultsmethod has been added to the base class, thus inherited by all phantom classes.The parameter
hi_contrast_thresholdhas been refactored tohigh_contrast_threshold.The attributes
lc_roisandhc_roishave been refactored tolow_contrast_roisandhigh_contrast_rois, respectively.The
analyzemethod now includes new standardized parametersangle_override,size_override, andcenter_override. Each of these is exactly what it sounds like: overriding pylinac’s automatic algorithm. This is useful if the automatic algorithm gives an incorrect value.A phantom outline is now displayed on images. This outline is a simple representation and should only be used as a guide to the accuracy of the phantom spatial detection. I.e. you can use this outline to potentially override the center, size, or angle based on the outline.
The automatic rotation analysis of the phantoms has been problematic. After spending a significant amount of time on the issue a satisfactory solution was not found. Therefore, the default angle or phantoms is that of the recommendation of the manufacturer. I.e. for the QC-3 phantom this means 45 degrees, as is the value when properly set up to the crosshairs.
High and low contrast ROIs now show as red if they were below the defined threshold.
Core Modules¶
A new core module
mtfhas been created to standardize all MTF calculations in pylinac. Previously, these were handled independently. The new module contains one classMTFwith one methodrelative_resolutionto calculate the lp/mm value at the passed rMTF percentage.
Bug Fixes¶
This release contains critical fixes. All users of the Winston-Lutz and VMAT modules are strongly encouraged to upgrade as soon as possible.
#268 The Winston-Lutz BB-finding method contained an error that would cause the BB center to be slightly off-center. After running unit tests, 5/16 datasets had a couch isocenter size difference of >0.2mm. Of those, 3 were around 0.2mm greater and 2 were around 0.2mm smaller. No other changes to iso sizes were detected within the testing tolerance of 0.2mm.
#204 The VMAT module was sometimes using raw pixel values to calculate the ROI deviations. This would cause the deviations to appear smaller than they should have been if the Rescale and Intercept had been applied to the pixel data.
#280 The Winston-Lutz 3D BB shift vector was underestimating the shifts by ~30-40%. A new 3D algorithm was implemented.
#275 Requirements no longer have an upper pinning, although scikit-image minimum version was bumped from 0.12 to 0.13.
#274 A new MTF module was created to refactor multiple ad hoc implementations.
#273 The CatPhan HU module detection algorithm was loosened slightly to account for very thin slice scans which have increased noise.
v 2.2.8¶
General¶
Although the following changes should really mean a 2.3 release, I consider them small enough that I will keep it a maintenance release.
An
invertparameter was added to theanalyzemethod of the FlatSym module so the user can override the automatic inversion.An
invertparameter was added to theanalyzemethod of the Starshot module so the user can override the automatic inversion.
Bug Fixes¶
#272 An
invertparameter was added to theanalyzefunction of the starshot module. This allows the user to force invert the image if pylinac’s auto-inversion algorithm is incorrect.#264/265 The
resultsmethod for the flatsym module would err out when images with 0 flatness were used.#191 The flatsym module was not loading non-DICOM images properly, causing processing failures.
#202 The rotation determination of the QC-3 phantom was often incorrect. This has temporarily been fixed by hardcoding the angle to 45 degrees. This is a correct assumption if the phantom is being used according to the instructions.
#263 The FlatSym module was sometimes incorrectly inverting images. This was fixed using a better histogram methodology.
#266 The deviation of a VMAT ROI was not properly detecting failing segments if the value was negative.
#267 The
overall_passedproperty of the CTP515 module contained an error that would cause an error.#271 The line pair/mm values for the CT/CBCT module was inadvertently doubled. I.e. the lines/mm was given, not line pairs.
v 2.2.7¶
Winston-Lutz¶
A small change was made to the Winston-Lutz BB finding algorithm to be more robust and use less custom code. The output from WL analyses should be within 0.1mm of previous values.
A section was added to the documentation to describe how images are classified and the analysis of output from the
.results()method.
Bug Fixes¶
#187 Scipy’s imresize function has been deprecated. Functionality was converted to use
skimage.transform.resize().#185 Winston-Lutz PDF generation had an artifact causing catastrophic failure.
#183 The Bakai fomula of the gamma calculation had an operational inconsistency such that dose-to-agreement other than 1% would give incorrect values of the gamma value.
#190 The Catphan module had an inconsistency in the rMTF/spatial resolution determination. Some line pair regions would be detected for some phantoms and not for others. This was caused by the different CatPhan models having slighly different rotations of the CTP528 module. Pylinac now has model-specific boundaries.
#192 The FlatSym plot would conflate the vertical and horizontal lines shown on the analyzed image. Analysis is unaffected, only the depiction of position.
#194 The Leeds low contrast ROI color on the analyzed image was not consistent with the contrast plots. ROI color is now based on the pass/fail of the contrast constant, not the contrast.
#196 Winston-Lutz images with a dense BB and low photon energy could cause BB detection to fail. A better BB-finding algorithm has been implemented.
#197 EPID RMS deviation would return 0 for the .results() method always. This now calculates correctly.
V 2.2.6¶
Bug Fixes¶
#157 This behavior is revered to pre-2.2.2 behavior to match the DFV and other software.
- #167 Originally, the fix for this was to raise an error and point to a workaround. At the time the fix was to add a parameter to v2.3.
Behavior was able to be changed internally to handle this case without an API change.
V 2.2.5¶
General¶
The watcher function has had several issues. It has been disabled and will be removed in v2.3.
Bug Fixes¶
#173 When forcing inversion of picket fence, the inversion came after the orientation determination, causing orientation to be wrong when inversion was needed.
#171 The
load_logfunction was not working correctly when passing a directory or ZIP archive.#172 Calling
publish_pdffrom log_analyzer without passing a filename would fail.#169 VMAT Dynalogs were calculating fluence incorrectly for CCW plans due to the gantry angle replacing the dose.
#160 While addressing #160 initially, Trajectory logs were unknowningly affected. Behavior has been reverted to pre-2.2.2 behavior and documentation changed.
V 2.2.4¶
Bug Fixes¶
#165 Machine log plots and PDFs showing the Leaf RMS were shown in cm, not in mm, as the axis title indicated.
#167 Picket fence images where the pickets are too close to the edge perpendicular to the pickets will fail. This adds an explicit error and mentions a workaround. The next major version will include a
paddingparameter to apply this workaround.#168 Picket fence analyses now crop 2 pixels from every edge. This will allow Elekta images to be analyzed since they inexplicably have a column of dead pixels in EPID images. Should not affect Varian images.
V 2.2.3¶
Bug Fixes¶
#158 Catphan roll determination algorithm has slightly widened the air bubble-finding criterion.
V 2.2.2¶
Bug Fixes¶
#157 Dynalog MLC leaf error was calculated incorrectly. Expected positions were off by a row. Error results should be lower on average.
#160 Dynalog MLC leaf internal pair mapping (1-61 vs 1-120) was different than documentation. Image calculations should not change.
#162 The LeedsTOR
angle_offsetin the.analyze()method was not being followed by the high-contrast bubbles.#144 The LeedsTOR angle determination is much more robust. Previously, only certain orientations of the phantom would correctly identify.
V 2.2.1¶
Bug Fixes¶
V 2.2.0¶
General¶
#131 Typing has been added to almost every function and class in pylinac.
F-strings have been incorporated. This bumps the minimum version for Python to 3.6.
The
publish_pdfmethod of every module has had its signature changed. Before, not all the signatures matched and only included a few parameters like author and unit name. This has been changed tofilename: str, notes: str, list of str, open_file: bool, metadata: dict. Filename and open file are straightforward. notes is a string or list of strings that are placed at the bottom of the report (e.g. ‘April monthly redo’). Metadata is a dictionary that will print both the key and value at the top of each page of the report (e.g. physicist and date of measurement)The TG-51 module has been placed under a new module: Calibration (TG-51/TRS-398). This is because:
A TRS-398 calibration module has been created TRS-398.
The default colormap for arrays is now Viridis, the matplotlib default.
A contributor’s guide has been added: Contributing.
#141 The Pylinac logo has been included in the package so that PDFs can be generated without needing www access.
A new dependency has been added: argue which handles input parameters.
Flatness & Symmetry¶
#130 The flatsym module has been completely rewritten. Documentation has also been updated and should be consulted given the number of changes: Field Analysis.
VMAT¶
The overall simplicity of use has been increased by automating & removing several parameters.
#128 The
VMATclass has been split into two classes:DRGSandDRMLC. Although there are now two classes instead of one, the overall simplicity has been increased, such as the following:The
testparameter inanalyze()is no longer required and has been removed.The
typeis no longer required in.from_demo_images().The demo method matches the other modules:
.run_demo()All naming conventions have been deprecated.
The
x_offsetparameter has been removed. The x-position is now based on the FWHM of the DMLC field itself. This means the x-position is dynamic and automatic.The
delivery_typesparameter has been removed. The delivery types of the images are now automatically determined.The methods for plotting and saving subimages (each image & the profiles) has been converted to a private method (
_plot_subimage(), …). There is little need for a public method to plot individually.
TG-51/Calibration¶
#127 A TRS-398 module has been added. There are two main classes:
TRS398PhotonandTRS398Electron.#129 The TG-51 module has been refactored to add a
TG51ElectronLegacyandTG51ElectronModerncalibration class. The Legacy class uses the classic TG-51 values that require a kecal value and a Pgradient measurement. The Modern class uses the equations from Muir & Rogers 2014 to calculate kQ that updates and incorporates the Pgradient and kecal values. While not strictly TG-51, these values are very likely to be incorporated into the next TG-51 addendum as the kQ values for photons already have.Certain parameters have been refactored:
volt_highandvolt_lowhave been refactored tovoltage_referenceandvoltage_reduced,m_raw,m_low, andm_opphave been refactored tom_reference,m_reduced, andm_opposite. These parameters are also the same for the TRS-398 classes (see #127).The
kqfunction has been separated into three functions:kq_photon_pdd10x,kq_photon_tpr2010, andkq_electron.A PDD(20,10) to TPR(20,10) converter function has been added:
tpr2010_from_pdd2010.Pressure and temperature conversion helper functions have been added:
mmHg2kPa,mbar2kPa,fahrenheit2celsius. This can be used in either TG-51 or TRS-398 to get TPR without actually needing to measure it.Defaults were removed from most functions to avoid possible miscalibration/miscalculation.
Most parameters of both TG-51 and TRS-398 were changed to be keyword only. This will prevent accidental miscalculations from simple positional argument mismatches.
Bug Fixes¶
V 2.1.0¶
General¶
After reflection, the package seems to have bloated in some respects. Certain behaviors are only helpful in very few circumstances and are hard to maintain w/ proper testing. They are described below or in their respective sections.
The command line commands have been deprecated. All commands were simply shortcuts that are just as easy to place in a 1-2 line Python script. There was no good use case for it in the context of how typical physicists work.
The interactive plotting using MPLD3 has been deprecated. Matplotlib figures and PDF reports should be sufficient. This was a testing nightmare and no use cases have been presented.
The transition of the method
return_results()toresults()is complete. This was baked-in from the very beginning of the package. It is expected that results would return something, nor is there any other corresponding method prefixed withreturn_.Pip is now the recommended way to install pylinac. Packaging for conda was somewhat cumbersome. Pylinac itself is just Python and was always installable via pip; it is the dependencies that are complicated. The wheels format seems to be changing that.
Some dependency minimum versions have been bumped.
CatPhan¶
The module was refactored to easily alter existing and add new catphan models.
The CatPhan HU module classifier has been deprecated. Its accuracy was not as high as the original brute force method. Thus, the
use_classifierkeyword argument is no longer valid.CatPhan 604 support was added thanks to contributions and datasets from Alan Chamberlain. More datasets are needed to ensure robust analysis, so please contribute your dataset if it fails analysis.
The CTP528 slice (High resolution line pairs) behavior was changed to extract the max value from 3 adjacent slices. This was done because sometimes the line pair slice selected was slightly offset from the optimum slice. Using the mean would lower MTF values. While using the max slightly increases the determined MTF from previous versions, the reproducibility was increased across datasets.
Winston-Lutz¶
Certain properties have been deprecated such as gantry/coll/couch vector to iso. These are dropped in favor of a cumulative vector.
A BB shift vector and shift instructions have been added for iterative WL testing. I.e. you can get a BB shift to move the BB to the determined iso easily.
import pylinac wl = pylinac.WinstonLutz.from_demo_images() print(wl.bb_shift_instructions()) # output: RIGHT 0.29mm; DOWN 0.04mm; OUT 0.41mm # shift BB and run it again...
Images taken at nonzero couch angles are now correctly accounted for in the BB shift.
Images now do not take into account shifts along the axis of the beam (#116).
The name of the file will now not automatically be interpreted if it can. This could cause issues for valid DICOM files that had sufficient metadata. If the image was taken at Gantry of 45 and the file name contained “gantry001” due to, e.g., TrueBeam’s default naming convention it would override the DICOM data. (#124)
Picket Fence¶
Files can now allow for interpretation by the file name, similar to the WL module. This is helpful for Elekta linacs that may be doing this test (#126).
Core Modules¶
is_dicomandis_dicom_imagewere moved from theutilitesmodule to theiomodule.field_edges()had the parameterinterpolationadded so that field edges could be computed more accurately (#123)A new class was created called
LinacDicomImage. This is a subclass ofDicomImageand currently adds smart gantry/coll/couch angle interpretation but may be extended further in the future.
V 2.0.0¶
General¶
Version 2.0 is here! It may or may not be a real major version update worthy of ‘2.0’, but ‘1.10’ just didn’t sound as good =)
A GUI has been added! Most major modules have been added to the GUI. The GUI is a very simple interface that will load files and publish a PDF/process files. To start the gui run the
gui()function like so:import pylinac pylinac.gui()
You may also start the GUI from the command line:
pylinac guiThe GUI is a result of a few causes. Many physicists don’t know how to code; this should remove that barrier and allow Pylinac to get even more exposure. I have always felt the web was the future, and it likely is, but pylinac should be able to run on it’s own, and because a rudimentary GUI is relatively easy, I’ve finally made it. The GUI is also free to use and has no hosting costs (unlike assuranceQA.com). Also, due to other ventures, a new job, and a newborn, I couldn’t devote further time to the assuranceQA site–A native GUI is much easier albeit much more primitive.
Some module PDF methods now don’t require filenames. If one is not passed it will default to the name of the file analyzed. E.g. “abc123.dcm” would become “abc123.pdf”. Modules where multiple images may be passed (e.g. a CBCT directory) still requires a filename.
PDF methods now have a boolean parameter to open the file after publishing:
open_file.A number of dependencies have been bumped. Some were for specific reasons and others were just out of good practice.
Watcher¶
Closes #84 Which would overwrite the resulting zip and PDF of initially unzipped CBCTs performed on the same day. I.e. multiple CBCTs would result in only 1 zip/PDF. The image timestamp has been edited so that it will include the hour-minute-second of the CBCT to avoid conflict.
Closes #86 - Which had a discrepancy between the YAML config setting of the file source directories and what the watcher was looking for.
CatPhan¶
Closes #85 Which displayed the nominal CBCT slice width on PDF reports, not the detected width for the CatPhan504 & CatPhan600.
Closes #89 which had variables swapped in the CatPhan503 PDF.
The
contrast_thresholdparameter has been renamed tocnr_threshold. The meaning and values are the same, but has been renamed to be consistent with other changes to theroimodule.Due to various problems with the SVM classifier, the default setting of the classifier has been set to
False.
Planar Phantoms¶
The Las Vegas phantom has been added to the planar imaging module. It’s use case is very similar to the existing planar phantoms:
from pylinac import LasVegas lv = LasVegas("myfile.dcm") lv.analyze() lv.publish_pdf() ...
The
pylinac.planar_imaging.LeedsTOR.analyze()method has an additional parameter:angle_offset. From analyzing multiple Leeds images, it has become apparent that the low contrast ROIs are not always perfectly set relative to the phantom. This parameter will allow the user to fine-tune the analysis to perfectly overlay the low contrast ROIs by adding an additional angle offset to the analysis.
Winston-Lutz¶
Closes enhancement #63 Files can now have the axis settings interpreted via the file name. E.g: “myWL_gantry90_coll0_couch340.dcm”. See Passing in Axis values for further info.
The
x/y/z_offsetproperties of the WLImages which were deprecated many versions ago have finally been removed.The
collimator/gantry_sagand associatedplot_gantry_sagmethods have been deprecated. A similar method has been implemented that utilizes the RMS deviation. To achieve the “gantry sag” using RMS errors use the methodaxis_rms_deviationwith parametervalue='range'.
TG-51¶
The Electron class has been adjusted to reflect the Muir & Rogers 2014 kecal data which allows the user to calculate kQ from just R50 data.
The
kqfunction now accepts anr_50parameter to calculate kQ based on the above data.
Core Modules¶
The
Imageclass has been fully deprecated and is no longer available. Use the functions available in the Image Module instead. See the version 1.4.0 release notes for further details.The
remove_edgesmethod has been deprecated and is now an alias forcrop. Thecropmethod should be used instead. Parameters are exactly the same.
V 1.9.0¶
General Changes¶
This release introduces PDF reports for most major modules. All classes with this functionality have been given a
publish_pdfmethod. This method takes an output filename and other optional data like the author, machine/unit, and any custom notes. See e.g.pylinac.starshot.Starshot.publish_pdf()orpylinac.picketfence.PicketFence.publish_pdf().The watch/process functions have been tweaked to best work on one unit per run. Multiple units/machines should have their own config files. A new article describes how to use the process function with Windows Task Scheduler to regularly pull and analyze files.
CatPhan¶
The CatPhan classes, when passed a directory during instantiation, will search through the DICOM files for Series UIDs and analyze the files of the most numerous UID. E.g. if a folder has 80 DICOM images including one set of 60 CBCT images and a total of 20 VMAT and picket fence images, it will find the CBCT files via UID and analyze those, leaving the other images/files alone. This is useful for when all QA images are simply dumped into one folder.
Raw, uncompressed CatPhan DICOM files can optionally be compressed to a ZIP file after analysis using the new
zip_afterargument in theanalyzemethod.
Watcher/Processer¶
The
watcher/processfunctions have been reworked to produce PDF files rather than PNG/txt files.If upgrading the watch/process function from a previous pylinac version be sure to copy/amend the new default YAML config file as new keywords have been added and using old YAML files will error out.
Several new configuration keywords have been changed/added. In the general section,
use-classifierhas been deprecated in favor of individual module keywords of the same name. This allows a user to use a classifier for, say, picket fence images but not for winston lutz images. Aunitkeyword has been added that specifies which unit the files should be considered to be from. This unit name is passed to the PDF reports that are generated. If you have multiple units, make individual YAML configuration files, one for each unit.CatPhan, VMAT, and Winston-Lutz can now take raw, unzipped images as well as the usual ZIP archive. ZIP archives are detected only by keywords as usual. For uncompressed CatPhan images, the analyzer will look for any CatPhan DICOM file groups via UID (see above CatPhan section), analyze them, and then ZIP the images until no further sets can be found. For VMAT and Winston-Lutz if the
use-classifiersetting is true their respective sections in the YAML configuration then an image classifier is used to group images of the given type and then analyze them.
v 1.8.0¶
General Changes¶
This release focuses solely on the CBCT/CatPhan module.
Pylinac now has a logo! Check out the readme on github or landing page on ReadTheDocs.
Watcher/Processer¶
The cbct analysis section has been renamed to
catphan. Thus, the YAML config file needs to look like the following:# other sections ... catphan: # not cbct: ... ...
CBCT/CatPhan¶
The Python file/module has been renamed to
ctfromcbct. E.g.:from pylinac.ct import ...
Most users import directly from pylinac, so this should affect very few people. This was done to generalize the module to make way for other CT/CBCT phantoms that pylinac may support in the future.
The CBCT module can now support analysis of the CatPhan 600.
Automatic detection of the phantom is no longer be performed. Previously, it depended on the manufacturer to determine the phantom (Varian->504, Elekta->503), but that did not consider users scanning the CatPhan in their CT scanners, which would give inconsistent results.
Due to the above, separate classes have been made for the CatPhan models. I.e. flow looks like this now:
# old way from pylinac import CBCT ... # new way from pylinac import CatPhan504, CatPhan600 cat504 = CatPhan504('my/folder') cat600 = CatPhan600.from_zip('my/zip.zip')
A classifier has been generated for each CatPhan. Thus, if loading a 503, a 503 classifier will be used, rather than a general classifier for all phantoms.
The
use_classifierparameter has been moved from theanalyze()method to the class instantiation methods like so:from pylinac import CatPhan504 cat504 = CatPhan504('my/folder', use_classifier=True) cat504.analyze() # no classifier argument
MTF is now more consistently calculated. Previously, it would simply look at the first 6 line pair regions. In cases of low mA or very noisy images, finding the last few regions would error out or give inconsistent results. Contrarily, high dose/image quality scans would only give MTF down to ~50% since the resolution was so good. Now, MTF is searched for region-by-region until it cannot find the correct amount of peaks and valleys, meaning it is now lost in the noise. This means high-quality scans will find and calculate MTF over more regions and fewer for low-quality scans. In general, this makes the MTF plot much more consistent and usually always gives the RMTF down to 0-20%.
Individual modules are now only composed of 1 slice rather than averaging the nearby slices. Previously, for consistency, a given module (e.g. CTP404) would find the correct slice and then average the pixel values of the slices on either side of it to reduce noise and give more consistent results. The drawback of this method is that results that depend on the noise of the image are not accurate, and signal/noise calculations were always higher than reality if only looking at one slice.
v 1.7.2¶
Fixed (#78) - Certain CBCT datasets have irregular background values. Additionally, the dead space in the square CT dataset outside the field of view can also be very different from the air background. This fix analyzes the dataset for the air background value and uses that as a baseline value to use as a CatPhan detection threshold.
V 1.7.0¶
General Changes¶
The underlying structure of the watcher script has been changed to use a different framework. This change allows for analysis of existing files within the directory of interest.
A new module has been introduced:
tg51, handling several common equations and data processing for things relating to TG-51 absolute dose calibration such as Kq, PDDx, Dref, pion, ptp, etc. It also comes with classes for doing a full TG-51 calculation for photons and electrons with cylindrical chambers.
Log Analyzer¶
The log analyzer has changed from having a main class of
MachineLog, to the two distinct log types:DynalogandTrajectoryLog. These classes are used the same way as machinelog, but obviously is meant for one specific type of log. This allows for cleaner source code as theMachineLogclass had large swaths of if/else clauses for the two log types. But don’t worry! If you’re unsure of the log type or need to handle both types then a helper function has been made:load_log. This function will load a log just like theMachineLogdid and as the new classes. The difference is it will do automatic log type detection, returning either a Dynalog instance or TrajectoryLog instance. TheMachineLogsclass remains unchanged.More specific errors have been introduced; specifically
NogALogError,NotADynalogError, andDynalogMatchErrorwhich are self-explanatory and more specific thanIOError.Fixed (#74) which was causing Dynalogs with patient names containing a “V” to be classified as Trajectory logs.
Fixed (#75) which was skewing gamma pass percent values.
Planar Imaging¶
The
PipsProQC3class/phantom has been refactored to correctly reflect its manufacturer to Standard Imaging, thus the class has been renamed toStandardImagingQC3.
Directory Watching¶
The
watchcommand line argument now has a sister function, available in a regular Python program:watch(). With this command you can run the directory watcher programmatically, perfect for continuous log monitoring.A new command line argument is available:
process. This command is also available in Python asprocess()which can be called on a directory either through the command line or programmatically and will analyze a folder once and then exit, perfect for analyzing a new monthly dataset.The structure of querying for files has been changed significantly. Instead of triggering on file changes (e.g. adding a new file to the directory), the watcher now constantly queries for new files at a specified interval. This means that when started, the watcher will analyze existing files in the folder, not just new ones.
Information given in the email has been modified for logs, which may potentially contain PHI. Instead of the entire log file name given, only the timestamp is given. Additionally, the logs are no longer attached to the email.
V 1.6.0¶
General Changes¶
Changed the default colormap of dicom/grayscale images to be “normal” gray vs the former inverted gray. Brought up in (#70) .
Added a colormap setting that can be changed. See Changing Colormaps
Added a utility function
clear_data_files()to clear demo files and classifier files. This may become useful for classifier updates. I.e. the classifier for a given algorithm can be cleared and updated as need be, without the need for a new package release. More information on this will follow as the use of classifiers becomes normal.Added a dependency to the pylinac requirements: scikit-learn. This library will allow for machine learning advancements to be used with pylinac. I am aware of the increasing number of dependencies; pylinac has reached a plateau I believe in terms of advancement and I hope that this is the last major dependency to be added.
Winston-Lutz¶
(#69) Added EPID position tracking. Now the EPID location will show up in images and will give an output value when printing the summary. Relevant methods like
cax2epid_distance()andepid_sag(), andplot_epid_sag()have been added. The summary plot has also been changed to include two sag plots: one for the gantry and one for the EPID.Certain properties of WL images have been deprecated.
x_offsethas been replaced bybb_x_offset()and respectively for the other axes. Usage of the old properties will raise a deprecation warning and will be removed in v1.7.Note
The deprecation warnings may not show up, depending on your python version and/or warning settings. See the python docs for more info.
CBCT¶
Added a Support Vector Machine classifier option for finding the HU slice. The classifier is faster (~30%) than the brute force method. This option is available as a parameter in the
analyze()method asuse_classifier. In the event the classifier does not find any relevant HU slices, it will gracefully fall back to the brute force method with a runtime warning. Because of the fallback feature, the classifier is now used first by default. Using the classifier requires a one-time download to the demo folder, which happens automatically; just make sure you’re connected to the internet.
Picket Fence¶
An
orientationkeyword argument was added to theanalyze()method. This defaults toNone, which does an automatic determination (current behavior). In the event that the determined orientation was wrong, this argument can be utilized.
Watcher Service¶
A new option has been added to the
generalsection:use-classifier. This option tells pylinac whether to use an SVM image classifier to determine the type of image passed. This allows the user not to worry about the file names; the images can be moved to the monitored folder without regard to naming. The use of the classifier does not exclude file naming conventions. If the classifier does not give a good prediction, the algorithm will gracefully fall back to the file name convention.The following image types currently support automatic detection:
Picket Fence
Starshot
Leeds TOR
PipsPro QC-3
V 1.5.6¶
Adds the
dtypekeyword toDicomImage’s init method.(#66) - Fixed an issue with Winston-Lutz isocenters not calculating correctly.
(#68) - Fixed the order of the Winston-Lutz images when plotted.
Many thanks to Michel for noting the WL errors and submitting the first external pull request !
Fixed several small bugs and runtime errors.
V 1.5.5¶
(#65) - Fixed the FlatSym demo file usage.
V 1.5.4¶
(#64) - Fixed the Picket Fence offset from CAX value, which previously were all the same value.
V 1.5.1-3¶
General Changes¶
Fixed conda entry points so that the user can use pylinac console scripts.
Moved demo images outside the package to save space. Files are downloaded when relevant methods are invoked.
V 1.5.0¶
General Changes¶
The pylinac directory watcher service got a nice overhaul. Now, rather than running the watcher script file directly, you can use it via the console like so:
$ pylinac watch "path/to/dir"
This is accomplished through the use of console scripts in the Python setup file. Once you upgrade to v1.5, this console command immediately becomes available. See the updated docs on Directory Watching. Previously, customizing behavior required changing the watcher script directly. Now, a YAML file can be generated that contains all the analysis configurations. Create and customize your own to change tolerances and even to trigger emails on analyses.
You can now anonymize logs via console scripts:
$ pylinac anonymize "path/to/log/dir"
This script is a simple wrapper for the log analyzer’s anonymize function.
Pylinac is now on anaconda.org – i.e. you can install via
condaand forget about dependency & installation issues. This is the recommended way to install pylinac now. To install, add the proper channel to the conda configuration settings.$ conda config --add channels jrkerns
Then, installation and upgrading is as simple as:
$ conda install pylinac
The advantage of saving the channel is that upgrading or installing in other environments is always as easy as
conda install pylinac.Pylinac’s core modules (
image,io, etc) are now available via the root package level.# old way from pylinac.core import image # new way from pylinac import image
Starshot¶
Relative analysis is no longer allowed. I.e. you can no longer pass images that do not have a DPI or SID. If the image does not have these values inherently (e.g. jpg), you must pass it explicitly to the Starshot constructor. No changes are required for EPID images since those tags are in the image file.
Added a
.from_zip()class method. This can contain a single image (to save space) or a set of images that will be combined.
Log Analyzer¶
The anonymize function received an optimization that boosted anonymization speed by ~3x for Trajectory logs and ~2x for Dynalogs. This function is very fast.
Trajectory log subbeam fluences are now available. This works the same way as for the entire log:
log = MachineLog.from_demo_dynalog() # calculate & view total actual fluence log.fluence.actual.calc_map() log.fluence.actual.plot_map() # calculate & view the fluence from the first subbeam log.subbeams[0].fluence.actual.calc_map() log.subbeams[0].fluence.actual.plot_map()
The gamma calculation has been refactored to use the image.gamma() method. Because of this, all
thresholdparameters have been changed to fractions:log = MachineLog.from_demo_trajectorylog() # old way log.fluence.gamma.calc_map(threshold=10) # <- this indicates 10% threshold # new way log.fluence.gamma.calc_map(threshold=0.1) # <- this also indicates 10% threshold
The gamma threshold parameter requires the value to be between 0 and 1, so any explicit thresholds will raise an error that should be addressed.
The
.pixel_mapattribute of the actual, expected, and gamma fluence structures have been renamed toarraysince they are numpy arrays. This attribute is not normally directly accessed so few users should be affected.
Bug Fixes¶
Fixed a bug that would not cause certain imaging machine logs (CBCT setup, kV setups) to be of the “Imaging” treatment type.
V 1.4.1¶
V 1.4.0¶
General Changes¶
Nearly all instance-based loading methods (e.g.
Starshot().load('myfile')) have been deprecated. Essentially, you can no longer do empty constructor calls (PicketFence()). The only way to load data is through the existing class-based methods (e.g.Starshot('myfile'),Starshot.from_url('http...'), etc). The class-based methods have existed for several versions, and they are now the preferred and only way as there is no use case for an empty instance.Since v1.2 most URLs were downloaded and then the local (but temporary) files were loaded. This practice has now been standardized for all modules. I.e. any
from_url()-style call downloads a temporary file and loads that. Because the downloads are to a temporary directory, then are removed upon exit.Loading images using the
Imageclass has been deprecated (but still works) in favor of the new functions in the same module with the same name. Where previously one would do:from pylinac.core.image import Image img = Image.load('my/file.dcm')
One should now do:
from pylinac.core.image import load img = load('my/file.dcm')
Functionality is exactly the same, but supports a better abstraction (there is no reason for a class for just behaviors). The same change applies for the other loading methods of the Image class:
load_urlandload_multiples. TheImageclass is still available but will be removed in v1.5.
Picket Fence¶
PicketFencecan now load a machine log along with the image to use the expected fluence to determine error. This means if an MLC bank is systematically shifted it is now detectable, unlike when the pickets are fitted to the MLC peaks. Usage is one extra parameter:pf = PicketFence('my/pf.dcm', log='my/pf_log.bin')
Winston-Lutz¶
A
from_url()method has been added.Upon loading, all files are searched within the directory, not just the root level. This allows for nested files to be included.
CBCT¶
The
from_zip_file()class constructor method has been renamed tofrom_zip()to be consistent with the rest of pylinac’s similar constructors.
Log Analyzer¶
A new
treatment_typehas been added for CBCT and kV logs:Imaging.A new function has been added to the module:
anonymize(). This function is similar to the.anonymize()method, but doesn’t require you to load the logs manually. The function is also threaded so it’s very fast for mass anonymization:from pylinac.log_analyzer import anonymize anonymize('my/log/folder') anonymize('mylog.bin')
Starshot¶
The starshot minimization algorithm has been changed from differential evolution to the more predictable minimize. Previously, results would often be predictable, but would occasionally give really good or really bad results even though no input was changed. This was due to the algorithm; now that a stable algorithm is being used, results are reproducible.
VMAT¶
The VMAT loading scheme got a few changes. The Naming Convention is still the same, but images are always loaded upon instantiation (see General Changes). Also, if the naming convention isn’t used, image delivery types can be passed in during construction; e.g.:
VMAT(images=(img1, img2), delivery_types=['open', 'dmlc']
Loading from a URL has been renamed from
from_urls()tofrom_url()and assumes it points to a ZIP archive with the images inside.
Bug Fixes¶
(#47) - Fixes the trajectory log number of beam holds calculation. Thanks, Anthony.
(#50) - Fixes RMS calculations for “imaging” trajectory logs. Previously, the RMS calculation would return
nan, but now returns 0.(#51) - Results of the starshot wobble were sometimes extremely high or low. This has been fixed by using a more stable minimization function.
(#52) - The starshot wobble diameter was incorrect. A recent change of the point-to-line algorithm from 2D to 3D caused this issue and has been fixed.
(#53) - The Winston-Lutz BB-finding algorithm would sometimes pick up noise, mis-locating the BB. A size criteria has been added to avoid detecting specks of noise.
(#54) - Imaging Trajectory logs, besides having no RMS calculation, was producing warnings when calculating the fluence. Since there is no fluence for kV imaging logs, the fluence now simply returns an 0’d fluence array.
(#55) - Dead pixels outside the field were throwing off the thresholding algorithm and not detecting the field and/or BB.
V 1.3.1¶
(#46) - Fixes CBCT analysis where there is a ring artifact outside the phantom. Incidentally, analysis is sped up by ~10%.
V 1.3.0¶
General Changes¶
A new dependency has been added: scikit-image. Given that pylinac is largely an image processing library, this is actually overdue. Several extremely helpful functions exist that are made use of in both the new modules and will slowly be incorporated into the old modules as needed. The package is easily installed via pip (
pip install scikit-image) or via conda (conda install scikit-image) if using the Anaconda distribution. Finally, if simply upgrading pylinac scikit-image will automatically install via pip. For the sake of installation speed I’d recommend conda.ROI sampling for CBCT and Leeds classes have been sped up ~10x, making analysis moderately to much faster.
All user-interface dialog functions/methods have been deprecated. E.g.
PicketFence.from_UI()is no longer a valid method. To retain similar functionality use Tk to open your own dialog box and then pass in the file name. Specifically, this applies to the VMAT, Starshot, PicketFence, MachineLog(s), FlatSym, and CBCT classes. The original goal of pylinac was to be used for a standalone desktop application. The assuranceqa.com web interface is the successor to that idea and does not need those UI methods.
Planar Imaging¶
A new planar imaging class has been added: PipsProQC3. This class analyzes the PipsPro QC-3 MV imaging phantom. The class locates and analyzes low and high contrast ROIs.
The Leeds phantom utilizes the scikit-image library to do a canny edge search to find the phantom. This will bring more stability for this class.
V 1.2.2¶
(#45) Fixes various crashes of Leeds analysis.
V 1.2.1¶
(#44) Fixed a stale wheel build causing
pip installto install v1.1.
V 1.2.0¶
General Changes¶
CatPhan 503 (Elekta) analysis is now supported.
A new planar imaging module has been added for 2D phantom analysis; currently the Leeds TOR phantom is available.
The
requestspackage is no longer needed for downloading URLs; the urllib stdlib module is now used instead.Requirements were fixed in the docs and setup.py; a numpy function was being used that was introduced in v1.9 even though v1.8 was stated as the minimum; the new requirement is v1.9.
Demonstration methods for the main classes have been fully converted to static methods. This means, for example, the following are equivalent:
CBCT().run_demo()andCBCT.run_demo().
Core Modules¶
A tutorial on the use of the core modules is now available.
A new
maskcore module was created for binary array operations.(#42) The Image classes now have a
gammamethod available.The Image classes’
median_filter()method has been renamed tofilter(), which allows for different types of filters to be passed in.The Image class can now load directly from a URL:
load_url().
CBCT¶
CatPhan 503 (Elekta) is now supported. Usage is exactly the same except for the low-contrast module, which is not present in the 503.
The low contrast measurements now use two background bubbles on either side of each contrast ROI. The default contrast threshold has been bumped to 15, which is still arbitrary but fits most eyeball values.
Starshot¶
(#43) Keyword arguments can be passed to the init and class methods regarding the image info. For example, if a .tif file is loaded but the DPI is not in the image header it can be passed in like so:
star = Starshot("mystar.tif", dpi=100, sid=1000)
Planar Imaging¶
2D analysis of the Leeds TOR phantom is available. Tests low and high contrast. A new Planar Imaging doc page has been created.
Winston-Lutz¶
A
save_summary()method has been added for saving the plot to file.
V 1.1.1¶
Winston-Lutz demo images were not included in the pypi package.
V 1.1.0¶
General Changes¶
This release debuts the new Winston-Lutz module, which easily loads any number of EPID images, finds the field CAX and the BB, and can plot various metrics.
Log Analyzer¶
Logs can now be anonymized using the
.anonymize()method for both MachineLog and MachineLogs.The
.to_csv()methods for MachineLog and MachineLogs returns a list of the newly created files.MachineLogs can now load from a zip archive using
.from_zip().
V 1.0.3¶
Fixes #39. MachineLog fluence was inverted in the left-right direction.
Fixes #40. MachineLog fluence calculations from dynalogs were dependent on the load order (A-file vs. B-file).
V 1.0.2¶
Fixes #38. MachineLog fluence calculations would crash if there was no beam-on snapshots (e.g. kV images).
V 1.0.1¶
Fixes #37. Reading in a trajectory log txt file with a blank line caused a crash.
V 1.0.0¶
General Changes¶
This release debuts the new interactive plotting for certain figures. Quickly, matplotlib line/bar plots (althouth not yet images/arrays) can be plotted and saved in HTML using the MPLD3 library. This is less of interest to users doing interactive work, but this adds the ability to embed HTML plots in web pages.
Several numpy array indexing calls were converted to ints from floats to avoid the new 1.9 numpy type-casting warnings. This also speeds up indexing calls slightly.
Picket Fence¶
The analyzed image now has the option of showing a leaf error subplot beside the image. The image is aligned to the image such that the leaves align with the image.
Starshot¶
Plotting the analyzed starshot image now shows both the zoomed-out image and a second, zoomed-in view of the wobble.
Each subplot can be plotted and saved individually.
VMAT¶
Plotting the analyzed image now shows the open and dmlc images and the segment outlines as well as a profile comparison between the two images. Each subplot can also be plotted and saved individually.
MLCSis no longer a test option;DRMLCshould be used instead.
V 0.9.1¶
Fixed a bug with the log analyzer treatment type property.
V 0.9.0¶
General Changes¶
This release has a few new features for the CBCT class, but is mostly an internal improvement. If you only use the main classes (CBCT, PicketFence, Starshot, etc), there should be no changes needed.
CBCT¶
The CBCT analysis now examines low contrast ROIs and slice thickness.
CBCT components have been renamed. E.g. the HU linearity attr has been renamed
hufromHU.
Starshot¶
Fixes #32 which was causing FWHM peaks on starshots to sometimes be erroneous for uint8/uint16 images.
PicketFence¶
Adds #31, a method for loading multiple images into PicketFence.
Log Analyzer¶
Fixes a bug which sometimes caused the parsing of the associated .txt log file for trajectory logs to crash.
V 0.8.2¶
Fixed a bug with the picket fence overlay for left-right picket patterns.
Plots for starshot, vmat, and picketfence now have a larger DPI, which should mean some more detail for saved images.
V 0.8.1¶
Fixed an import bug
V 0.8.0¶
General Changes¶
An upgrade for the robustness of the package. A LOT of test images were added for the Starshot, CBCT, PicketFence, and VMAT modules and numerous bugs were caught and fixed in the process.
The debut of the “directory watcher”. Run this script to tell pylinac to watch a directory; if a file with certain keywords is placed in the directory, pylinac will analyze the image and output the analyzed image and text file of results in the same directory.
A generic troubleshooting section has been added to the documentation, and several modules have specific troubleshooting sections to help identify common errors and how to fix them.
VMAT¶
Added a
from_zip()andload_zip()method to load a set of images that are in a zip file.Added an
x_offsetparameter toanalyze()to make shifting segments easier.
PicketFence¶
Fixed #30, which wasn’t catching errors on one side of the pickets, due to a signed error that should’ve been absolute.
Two new parameters have been added to
analyze():num_picketsandsag_adjustment, which are somewhat self-explanatory. Consult the docs for more info.
Starshot¶
Fixed #29, which was causing analysis to fail for images with a pin prick.
CBCT¶
Fixed #28, which was applying the phantom roll adjustment the wrong direction.
V 0.7.1¶
General Changes¶
Added
.from_url()class method and.load_url()methods to most modules.
PicketFence¶
Fixed #23, which was not properly detecting pickets for picket patterns that covered less than half the image.
Fixed #24, which was failing analysis from small but very large noise. A small median filter is now applied to images upon loading.
V 0.7.0¶
General Changes¶
The scipy dependency has been bumped to v0.15 to accommodate the new differential evolution function using in the Starshot module.
CBCT¶
Whereas v0.6 attempted to fix an issue where if the phantom was not centered in the scan it would error out by adding a z-offset, v0.7 is a move away from this idea. If the offset given was not correct then analysis would error disgracefully. It is the point of automation to automatically detect things like where the phantom is in the dataset. Thus, v0.7 is a move towards this goal. Briefly, upon loading all the images are scanned and the HU linearity slice is searched for. Of the detected slices, the median value is taken. Other slices are known relative to this position.
As per above, the z-offset idea is no longer used or allowed.
Plots are now all shown in grayscale.
If the phantom was not completely scanned (at least the 4 modules of analysis) analysis will now error out more gracefully.
V 0.6.0¶
General Changes¶
Pylinac now has a wheel variation. Installation should thus be quicker for users with Python 3.4.
Most main module classes now have a save method to save the image that is plotted by the plot method.
Class-based Constructors¶
This release presents a normalized and new way of loading and initializing classes for the PicketFence, Starshot, VMAT and CBCT classes. Those classes all now accept the image path (folder path for CBCT) in the initialization method. Loading other types of data should be delegated to class-based constructors (e.g. to load a zip file into the CBCT class, one would use
cbct = CBCT.from_zip_file('zfiles.zip')). This allows the user to both initialize and load the images/data in one step. Also prevents user from using methods before initialization (i.e. safer). See ReadTheDocs page for more info.
Dependencies¶
Because the VMAT module was reworked and is now based on Varian specs, the pandas package will no longer be required. FutureWarnings have been removed.
CBCT¶
Bug #18 is fixed. This bug did not account for slice thickness when determining the slice positions of the relevant slices.
Bug #19 is fixed. This bug allowed the loading of images that did not belong to the same study. An error is now raised if such behavior is observed.
Demo files are now read from the zipfile, rather than being extracted and then potentially cleaning up afterward. Behavior is now quicker and cleaner.
Individual plots of certain module/slices can now be done. Additionally, the MTF can be plotted.
The user can now adjust the relative position of the slice locations in the event the phantom is not set up to calibration conditions.
Log Analyzer¶
Keys in the
txtattr dict weren’t stripped and could have trailing spaces. Keys are now stripped.
VMAT¶
- Ability to offset the segments has been added.
Complete overhaul to conform to new Varian RapidArc QA specs. This includes the following:
Rather than individual samples, 4 or 7 segments are created, 5x100mm each.
Deviation is now calculated for each segment, based on the average segment value.
The
DRMLCtest has changed name toMLCS. E.g. passing a test should be:myvmat.analyze('mlcs'), notmyvmat.analyze('drmlc'); the latter will still work but raises a future warning.
Starshot¶
Fixed a bug where an image that did not have pixels/mm information would error out.
Added a tolerance parameter to the analyze method.
V 0.5.1¶
Log Analyzer¶
Axis limits are now tightened to the data when plotting log_analyzer.Axis data.
Gamma map plot luminescence is now normalized to 1 and a colorbar was added.
Bug #14 fixed, where Tlogs v3 were not loading couch information properly.
Trajectory log .txt files now also load along with the .bin file if one is around.
Starshot¶
Multiple images can now be superimposed to form one image for analysis.
VMAT¶
load_demo_image()parameter changed fromtest_typetotype
V 0.5.0¶
A new flatness & symmetry module allows for film and EPID image analysis.
The
log_analyzermodule now supports writing trajectory logs to CSV.A FutureWarning that pandas will be a dependency in later versions if it’s not installed.
V 0.4.1¶
Batch processing of logs added via a new class.
~4x speedup of fluence calculations.
V 0.4.0¶
A Varian MLC picket fence analysis module was added; this will analyze EPID PF images of any size and either orientation.
V 0.3.0¶
Log Analyzer module added; this module reads Dynalogs and Trajectory logs from Varian linear accelerators.
Starshot¶
The profile circle now aligns with the lines found.
Recursive option added to analyze for recursive searching of a reasonable wobble.
Image now has a cleaner interface and properties
V 0.2.1¶
Demo files were not included when installed from pip
V 0.2.0¶
Python 2.7 support dropped. Python 3 has a number of features that Python 2 does not, and because this project is just getting started, I didn’t want to support Python 2, and then eventually drop it as Python 3 becomes more and more mainstream.
Internal overhaul. Modules are now in the root folder. A core module with specialized submodules was created with a number of various tools.
Demo files were assimilated into one directory with respective subdirectories.
VMAT module can now handle HDMLC images.
CBCT module was restructured and is much more reliable now.
method names normalized, specifically the
return_resultsmethod, which had different names in different modules.Lots of tests added; coverage increased dramatically.
V 0.1.3¶
Overall
A module for analyzing CBCT DICOM acquisitions of a CatPhan 504 (Varian) has been added. The starshot demo files have been compressed to zip files to save space. A value decorator was added for certain functions to enforce, e.g., ranges of values that are acceptable. The “Files” directory was moved outside the source directory. -Starshot now reports the diameter instead of radius
V 0.1.2¶
A PyPI setup.py bug was not properly installing pylinac nor including demo files. Both of these have been fixed.
V 0.1.1¶
Several small bugs were fixed and small optimizations made. A few methods were refactored for similarity between modules.
V 0.1.0¶
This is the initial release of Pylinac. It includes two modules for doing TG-142-related tasks: Starshot & VMAT QA
Versioning mostly follows standard semantic revisioning. However, each new module will result in a bump in minor release, while bug fixes will bump patch number.